Anatomy Mock Exam 1
- On
- InEmbryology / Gross anatomy / Histology / Mock Exams
Reviewed by Dr Jeffrey Kalei





Overview Purines are nitrogen-containing heterocyclic bases that form part of nucleotides. They have a double-ring structure (6-membered ring fused to a 5-membered ring) Precursors for de novo purine ring synthesis Precursor Contribution Glycine C4, C5, N7 Glutamine N3, N9 Aspartate…
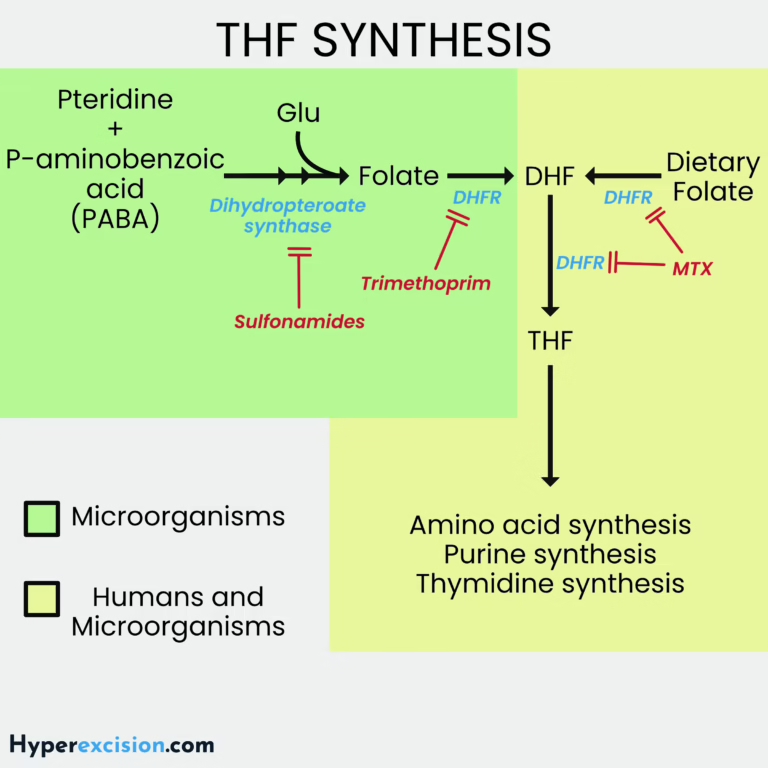
Tetrahydrofolate Synthesis Tetrahydrofolate (THF) is essential for purine synthesis and thymidylate (dTMP) formation, both of which are important for DNA synthesis. THF synthesis in Bacteria vs Humans Category Description Bacteria Must synthesize folate de novo Humans Cannot synthesize folate de…