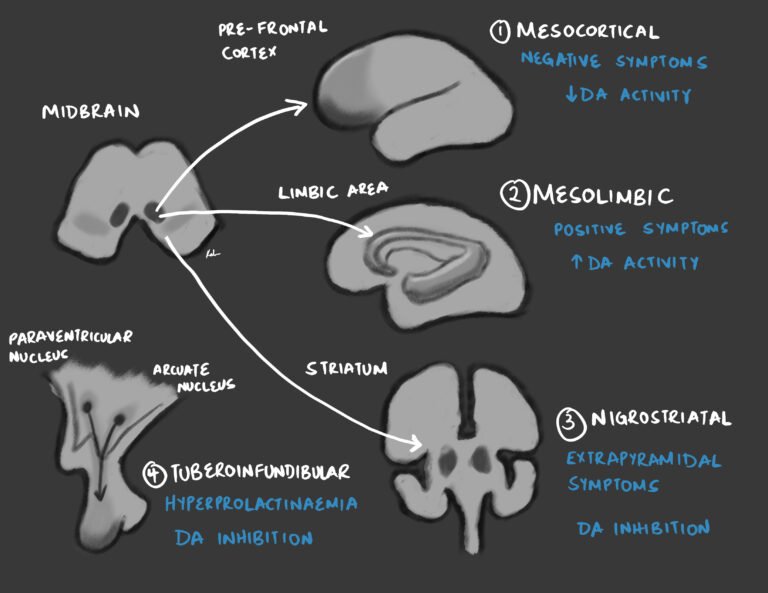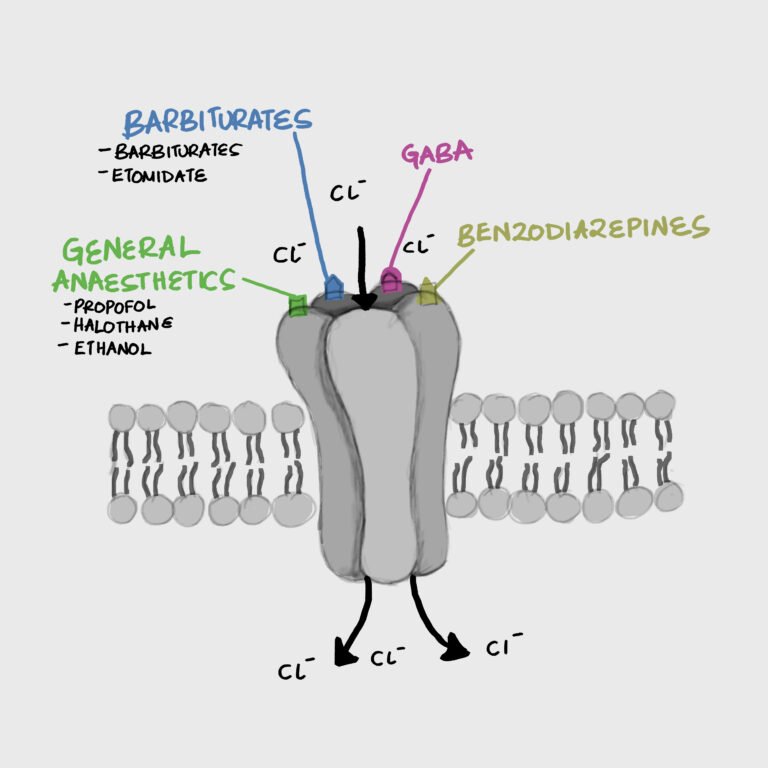
Anxiolytics
Overview Anxiolytics Nota bene Benzodiazepines Widely used for panic disorders, anxiety disorders, Insomnia and Status epilepticus Barbiturates Rarely used. First-line for infantile seizures, and second-line for status epilepticus. Were originally used for insomnia and panic disorders but fell out of…