Endometriosis
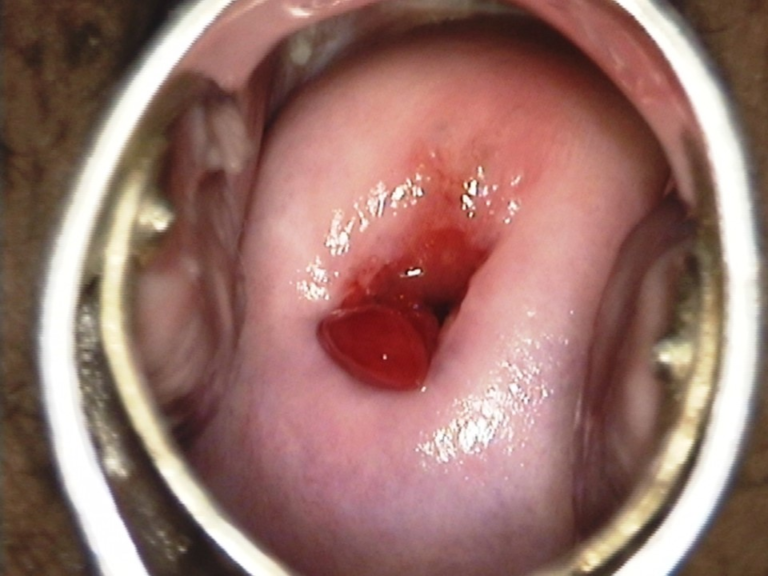
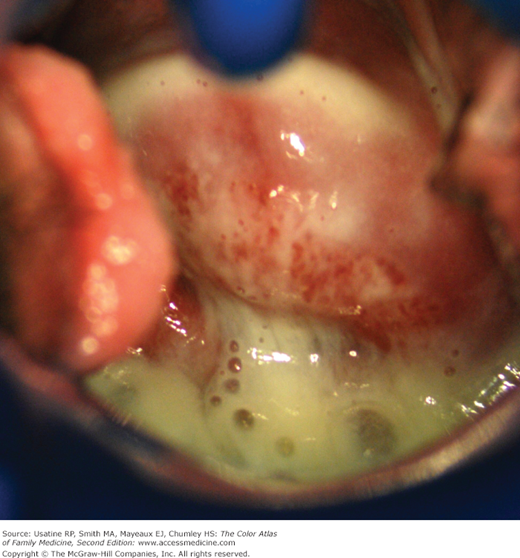
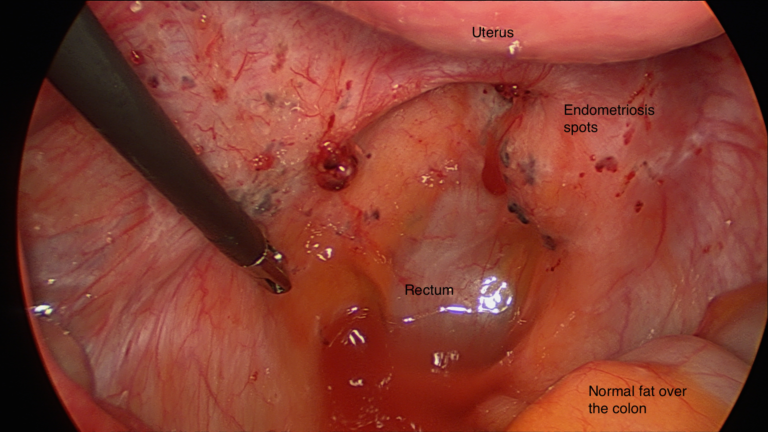
Endometriosis is the presence of endometrial glands and stroma outside the normal location, excluding adenomyosis. It is a hormonally dependent disease, and therefore commonly presents as cyclical pelvic pain. Prevents chiefly in women of reproductive age. Should be considered as…