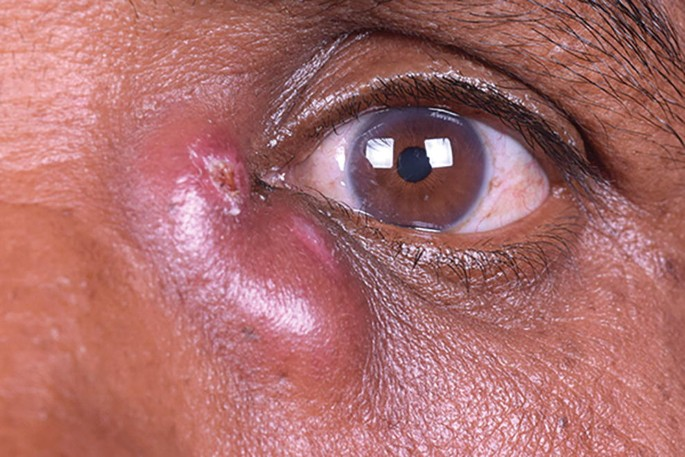
Dacryocystitis
Overview Dacyrocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac usually as a result of obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct. It is the most frequent disorder affecting the lower lacrimal system and usually occurs unilaterally. It may present acutely or chronically…

