Anaemia

Anaemia is defined as a decrease in red cell mass as evidenced by low haemoglobin concentration in blood below the reference range for a given age or sex in a given population or geographic location. WHO gives the reference value…

Anaemia is defined as a decrease in red cell mass as evidenced by low haemoglobin concentration in blood below the reference range for a given age or sex in a given population or geographic location. WHO gives the reference value…
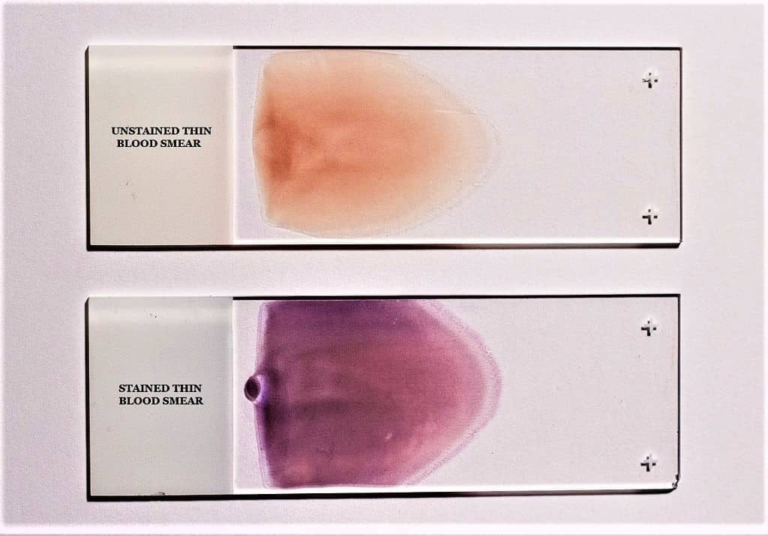
Centrifugation Serum Plasma Definition Liquid that remains after blood has clotted Liquid that remains when clotting is prevented Preparation Centrifuge clotted blood Centrifuge whole blood with anticoagulant Fibrinogen Absent Present Complete Blood Count Peripheral blood film A PBF is a…
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Pelvic inflammatory disease is a subacute to chronic infectious disease that affects the upper female reproductive tract (cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries) and/or peritoneum. The most common causative organisms are C. trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, but most cases can be polymicrobial (involving…
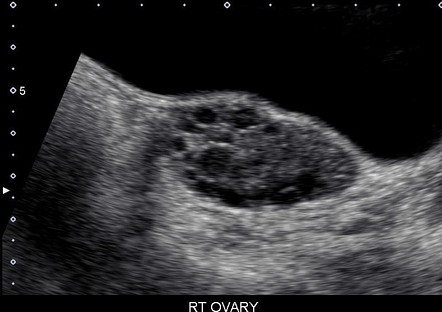
PCOS is a genetic, hormonal, metabolic, *and *reproductive disorder. It is the most common endocrine disorder of women in reproductive age. Etiology is unknown but there is a genetic component. Endocrine/hormonal disturbances lead to a constellation of sx. Sx vary…
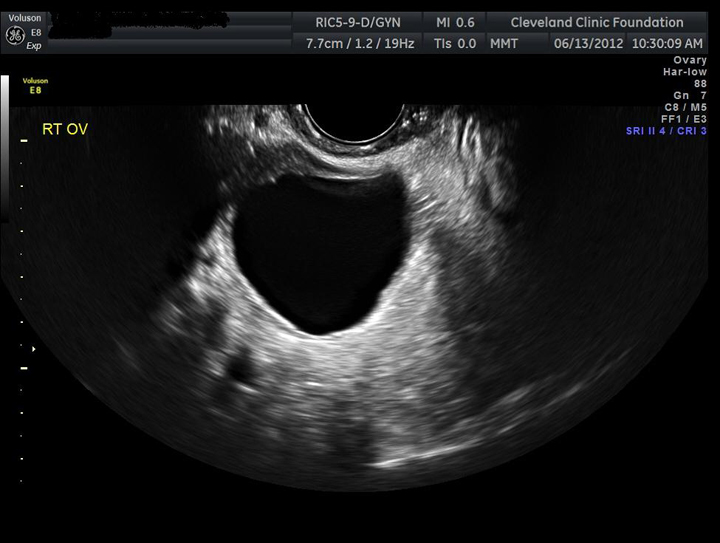
Overview Benign mass Malignant mass Size < 8cm > 8cm Consistency Cystic Solid or mixed Solid component None Nodular, Papilary Sepatations None or single Multilocular, thick Doppler Negative Positive Laterality Unilateral Bilateral (50% of tumors) Associated Fx Calcification Ascites, Peritoneal…
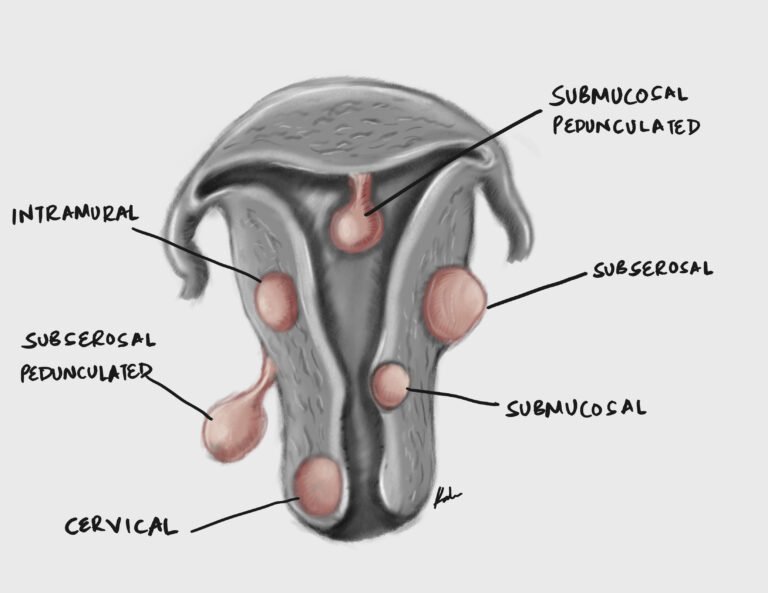
Fibroids are benign smooth muscle neoplasms arising from myometrial cells. Usually clinically insignificant but VERY common (it is the most common benign tumour in women). Average growth is 0.5 cm Fibroids are estrogen and progesterone-sensitive (similar to endometriosis and adenomyosis).…
Endometrial cancer is the most common cancer of the female genital tract and the fourth most common cause of cancer overall in women. 3% of women will develop endometrial cancer in their lifetime. 75% of endometrial cancers are adenocarcinomas (arising…
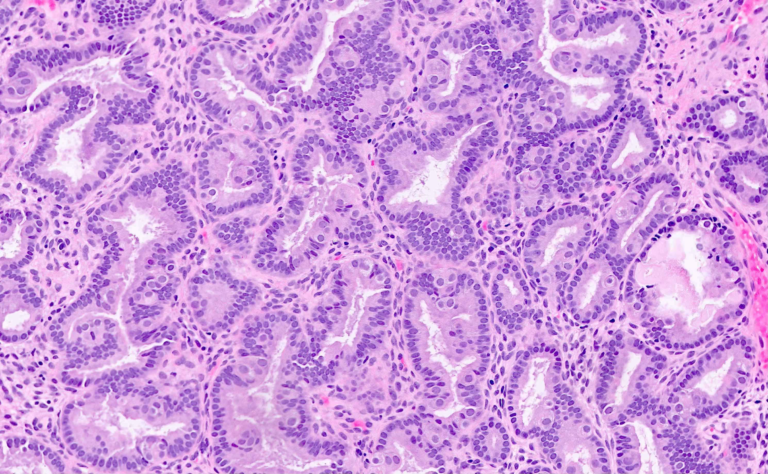
Endometrial hyperplasia is endometrial thickening with a proliferation of irregularly sized and shaped glands. Tends to be symptomatic in post-menopausal women. Endometrial hyperplasia in a post-menopausal woman (around 10mm) would be a normal endometrial thickness for a pre-menopausal woman in…
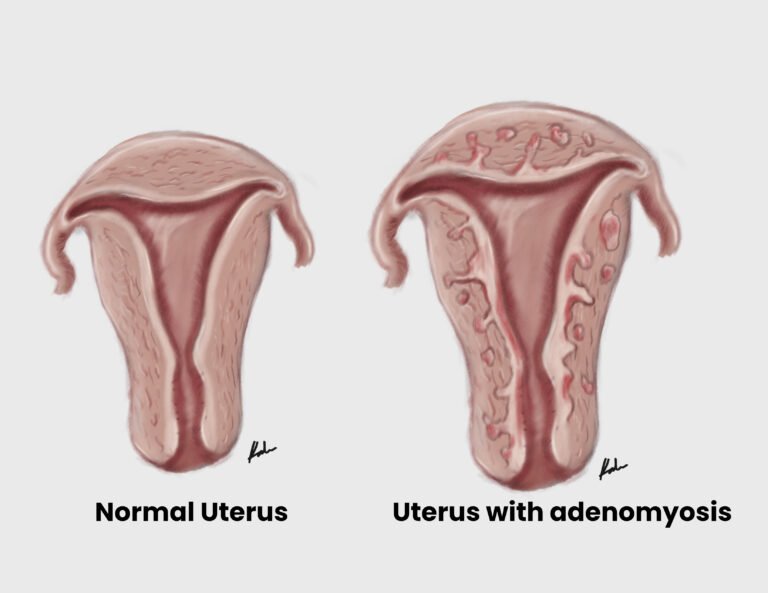
Adenomyosis is uterine enlargement caused by focal or diffuse ectopic rests of endometrial tissue within the myometrium. Pathogenesis is not fully understood. Most likely due to direct invasion of the endometrium into the myometrium. The most common symptoms are abnormal…
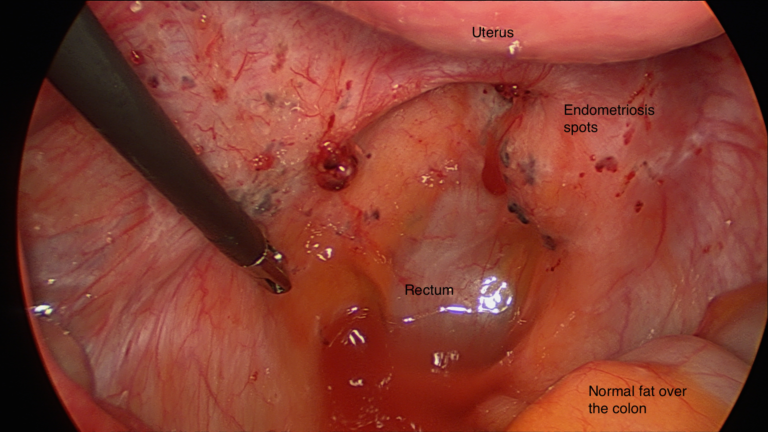
Endometriosis is the presence of endometrial glands and stroma outside the normal location, excluding adenomyosis. It is a hormonally dependent disease, and therefore commonly presents as cyclical pelvic pain. Prevents chiefly in women of reproductive age. Should be considered as…