


On Finding Purpose in Medicine
I have a confession. I did not choose to study medicine. Well, technically, I did. Kind of. Allow me to explain. Like many other young children, I floated between endless possibilities of what I wanted to be when I grew…
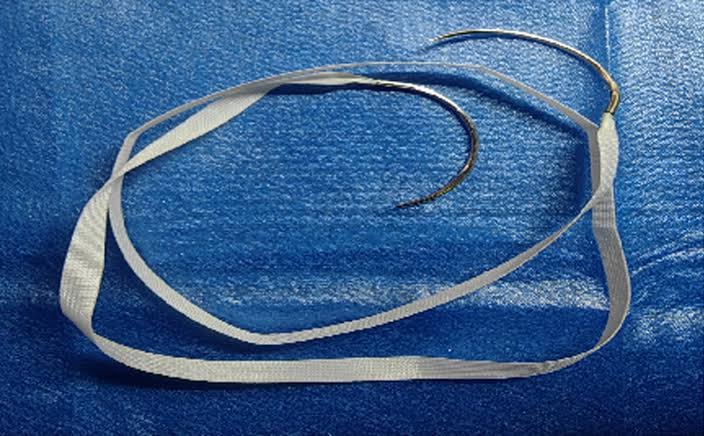

Cervical Incompetence
Cervical incompetence Cervical incompetence is the inability of the cervix to hold closed during pregnancy. When there is incompetence, the cervix spontaneously opens up leading to spontaneous expulsion of the fetus. Cervical incompetence leads to recurrent preterm birth or second…



Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is characterized by two or more psychotic symptoms for 6 months or more. Symptoms can be delusions, hallucinations (mainly auditory), disorganized speech, disorganized or catatonic behaviour, and negative symptoms (affective flattening, avolition, mutism). They severely impact daily life…

Forensic Psychiatry
Overview As per the Royal College of Pychiatrists, Forensic Psychiatry is a specialty which helps mentally disordered people who are a risk to the public. Forensic psychiatrist work side by side with the police, courts and prisons. A Forensic Pyschiatrist…
