- List the modes of formation of bone tissue
- Intramembranous ossification
- Endochondral ossification
Distinguish between endochondral and membranous ossification. Give examples
| Endochondral ossification | Intramembranous ossification | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Development of bone tissue within cartilage | Development of bone tissue within mesenchymal tissue without cartilage formation |
| Mechanism | Cartilage is formed first and bone is laid on it | Bone is directly formed from mesenchyme |
| Intermediate cartilage | Yes | No |
| Types of bones formed | Long bones | Flat bones |
| Chondrocytes involved | Yes | No |
| Osteoclasts involved | Yes | No |
| Components of the skeleton formed | Long bones of the extremities and axial skeleton | Skull, face, mandible and clavicles |
Distinguish between interstitial and appositional growth of cartilage
| Interstitial Growth | Appositional growth | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increase in bone length | Increase in bone width |
| Growth from | Within | Outside |
| Location | Lacunae | Pre-existing cartilage |
| Mechanism | Chondrocytes within divide and secrete matrix. Cartilage lengthens and is replaced by bone tissue | Chondroblasts in the perichondrium secrete matrix. New bone tissue is deposited on the surface of pre-existing bone |
| Outcome | Longer bones | Thicker bones |
What are the structural differences between mature and immature bone
| Mature Bone | Immature Bone | |
|---|---|---|
| Organization | Lamellar bone | Woven bone |
| Cells per unit area | Less | More |
| Arrangement of cells | Arranged in their long axes in the same direction as Lamellae | Randomly arranged |
| Ground substance | Less | More |
- Name the cell types in bone tissue and their respective functions
- Osteoprogenitor cells: Osteogenesis – formation of new bone
- Osteoblasts: The differentiated bone forming cell – deposits bone matrix
- Osteocytes: The mature bone enclosed by bone matrix
- Bone-lining cells: derived from osteoblasts. Cover bone where remodeling is not occurring.
- Osteoclasts: Resorption of bone and remodeling.
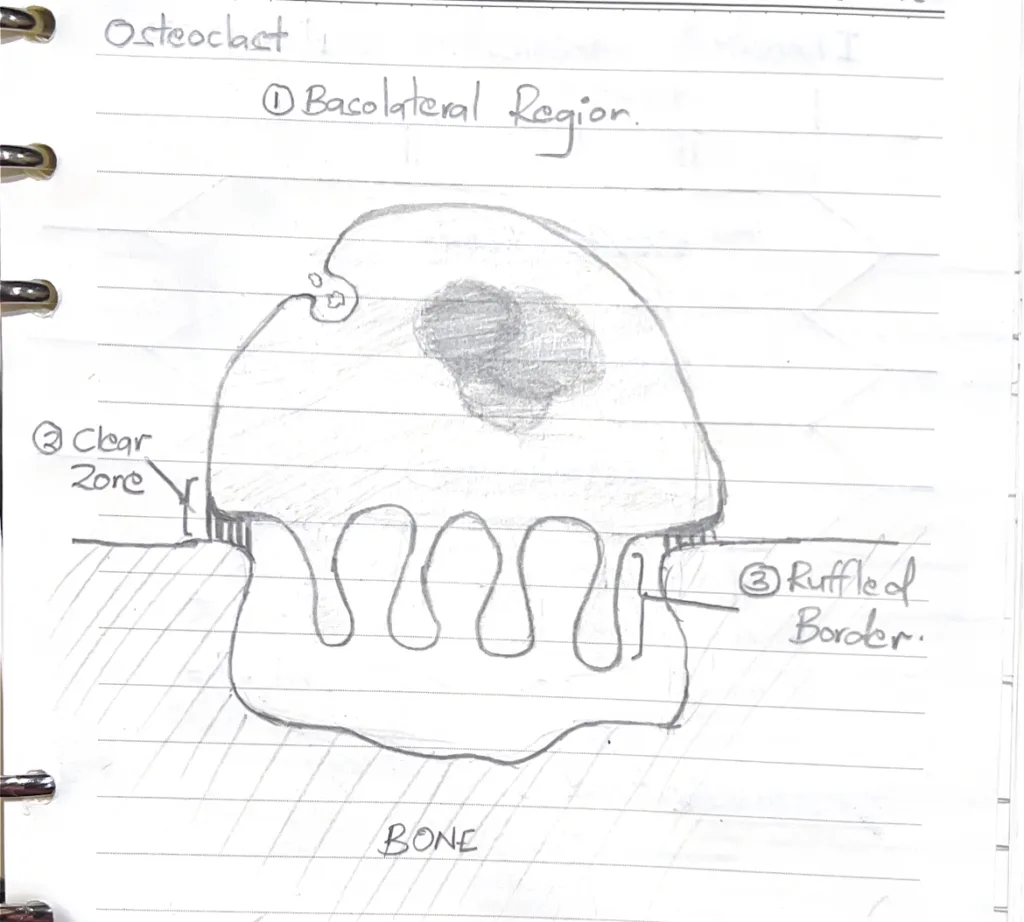
- Name the functional zones of an active osteoclast
- Ruffled border
- Clear zone
- Basolateral region
- Illustrate the morphological features of an active osteoclast
- Describe the zonation of the epiphyseal growth plate
- Zone of reserve cartilage: No cellular proliferation or active matrix production
- Zone of proliferation: Chondrocytes undergo division and organize into distinct columns
- Zone of hypertrophy: Contains hypertrophic chondrocytes which have accumulated glycogen
- Zone of calcified cartilage: Chondrocytes undergo apoptosis and the matrix becomes mineralized
- Zone of resorption: Calcified cartilage here is in direct contact with the connective tissue of the marrow cavity. It is invaded by osteoprogenitor cells which occupy the spaces previously filled by the dead chondrocytes.
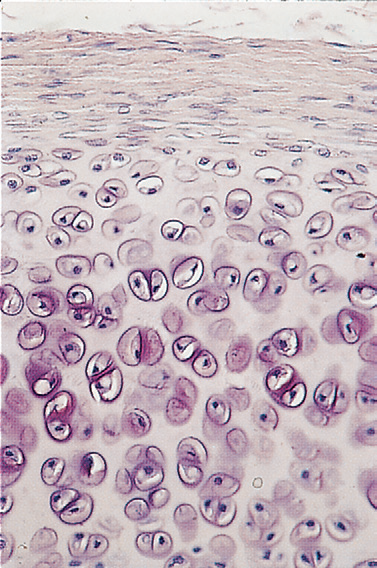
- Name 2 zones of the epiphyseal growth plate that are involved in cell quiescence and cell death
- Cell quiescence: Zone of reserve cartilage
- Cell death: Zone of calcified cartilage

