Table Of Contents
Fistula in Ano
A Fistula-in-ano is a communication between the anal canal and perianal skin. They are a notorious complication of perianal abscess and Crohn’s disease. It can occur at the site of a drain placement or at the incision used to drain the abscess. Fistula-in-ano can result in recurrent abscesses. Patients are often bothered by purulent or feculent drainage from the external opening. The location of the internal opening can be determined using Goodsall’s rule. Diagnosis is clinical.
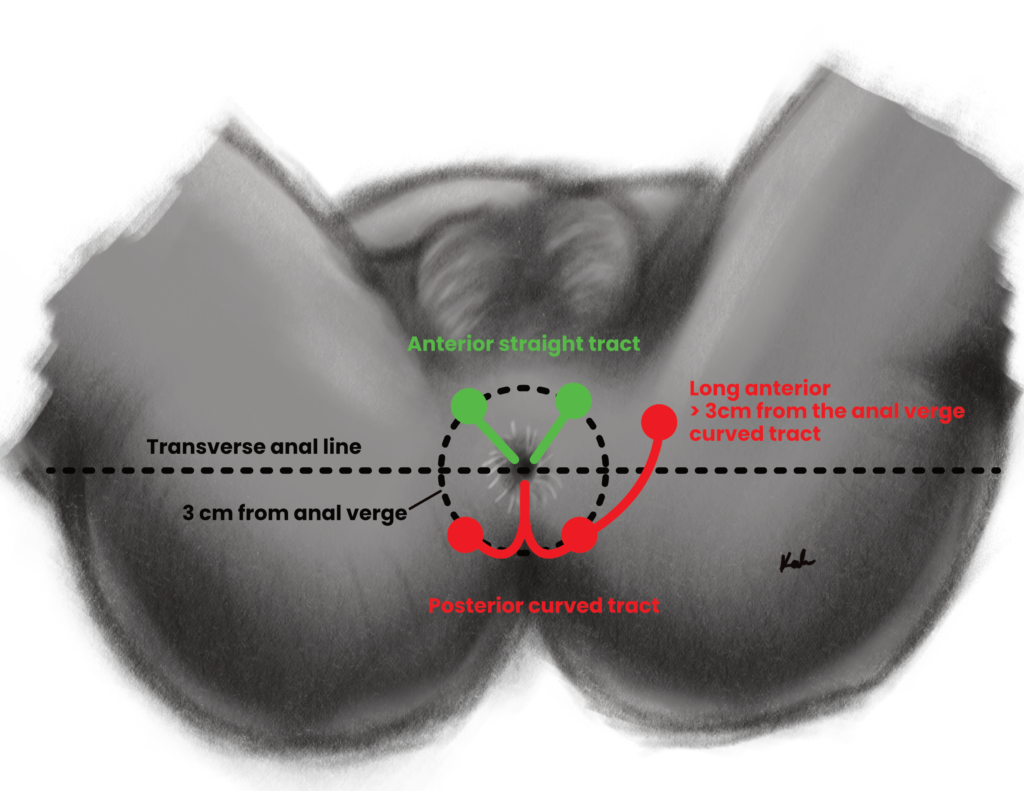
Goodsall’s rule for fistula in ano
| Opening in relation to transverse anal line | Tract |
|---|---|
| Anterior opening | Travels in a radial (straight) path to the anal canal |
| Posterior opening | Travels in a curved tract to the anal canal. PC = Posterior opening takes a Convoluted course |
| Opening more than 3 cm from the anus | May travel in a curved tract to the anal canal |
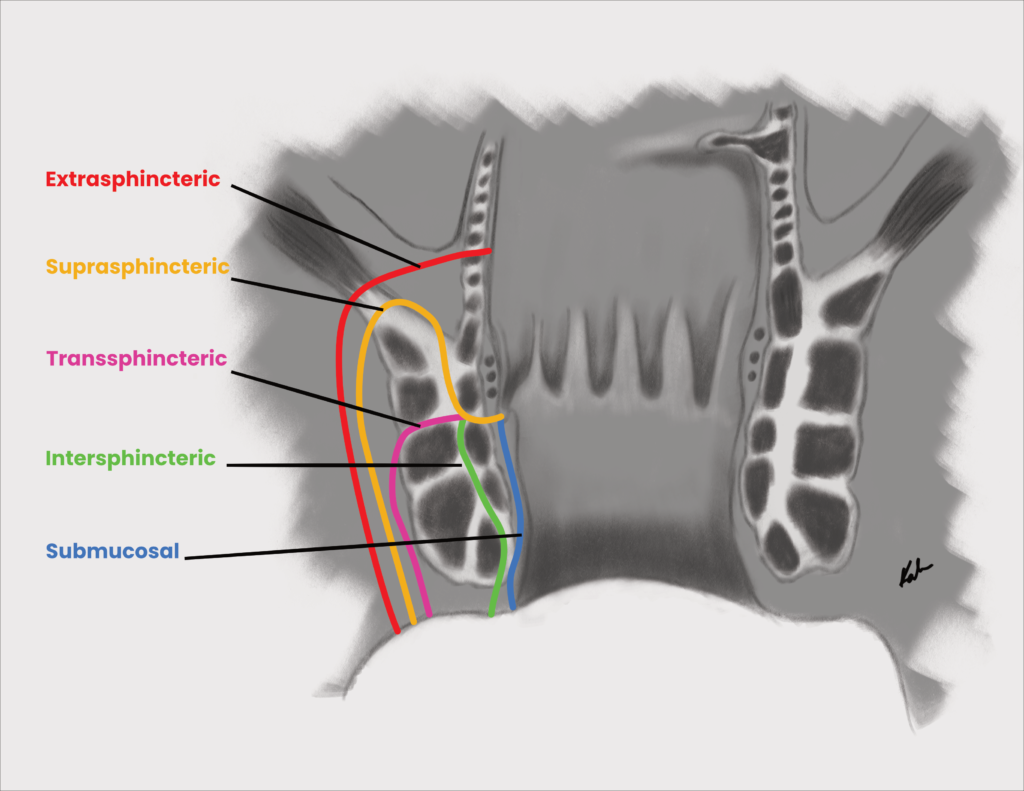
Classification of fistula in ano (Park’s)
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
| Intersphincteric | Penetrates internal sphincter to intersphincteric space |
| Transsphincteric | Penetrates internal and external sphincters to ischiorectal fossa |
| Suprasphincteric | Penetrates levator ani |
| Extrasphincteric | From the rectum above the dentate line through the levator ani |
- Signs and symptoms
- Feculent or purulent peri-anal discharge
- Perianal or rectal pain
- Swelling
- Bleeding
- External opening visible
- Investigations
- Proctosigmoidoscopy or anoscopy under anaesthesia: for formal diagnosis
- Treatment
- Fistulotomy: cut along the length of the fistula to open it. Leave to heal by secondary intention.
- Seton placement (cutting or draining): placed to keep the fistula tract open, ensure adequate drainage and fibrosis (healing). Cutting setons slowly divide the fistula while maintaining continence
- Fibrin glue or fistula plug: provides scaffolding for collagen deposition,
- Treat the underlying cause e.g. crohn’s disease
- Antibiotics
- Indications for fistulotomy
- Intersphincteric and low transphincteric fistulas
- Indications for seton placement
- High transsphincteric, suprasphincteric and extrasphincteric fistula

