- List the layers of the cornea
- Corneal epithelium
- Bowman’s membrane (anterior basement membrane)
- Corneal stroma
- Descemet’s membrane (Posterior basement membrane)
- Corneal epithelium
- List the layers of the sclera
- Episclera
- Tenon’s space (episcleral space)
- Tenon’s capsule (substantia proper/ sclera proper)
- Lamina fusca (suprachoroid lamina)
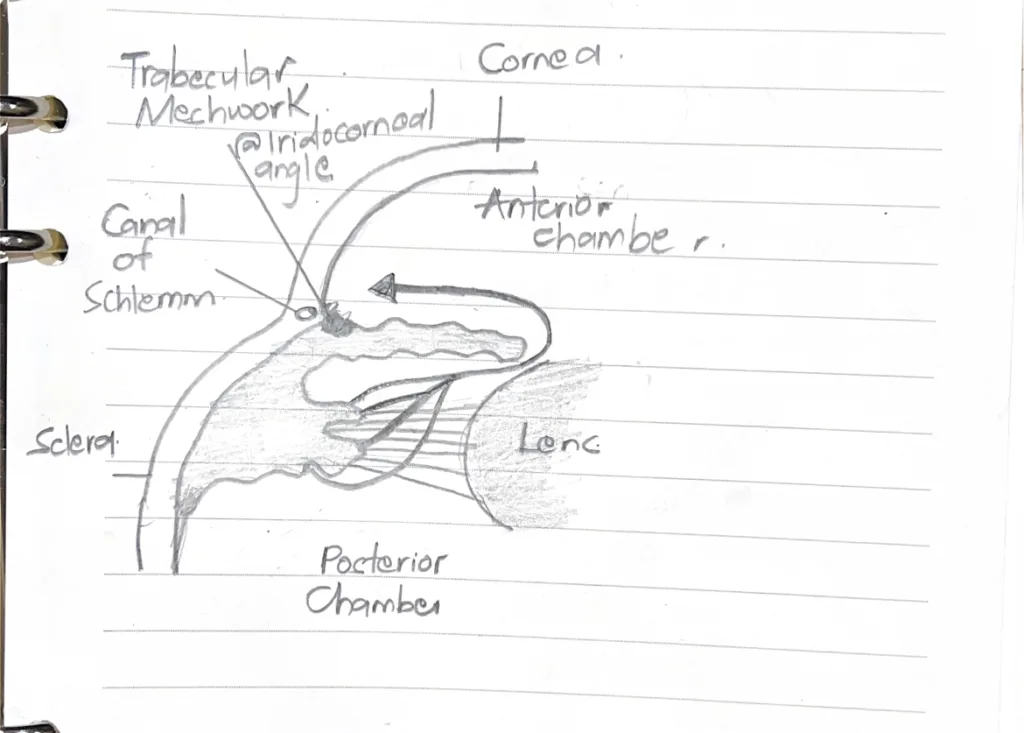
- Where is aqueous humor formed, how does it flow and where is it drained? State its function
- Formation: Ciliary body
- Flow: ciliary body → lens → posterior chamber → anterior chamber → iridocorneal angle
- Drainage: Iridocorneal angle → limbus → trabecular meshwork → canal of schlemm
- Functions
- Maintains intraocular pressure
- Nutrition
- Remove metabolites from avascular tissues of the cornea and lens
- What are the functions of the ciliary body/ epithelium
- Secretes aqueous humor
- It is a component of the blood-ocular barrier
- It secretes and anchors the zonula fibers, which form the suspensory ligaments of the lens
- It regulates lens thickness (ciliary muscles)
- In sequence, name the ten layers of the retina
- Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
- Layer of rods and cones
- Outer Limiting membrane
- Outer nuclear layer
- Outer plexiform layer
- Inner nuclear layer
- Inner plexiform layer
- Ganglion cell layer
- Layer of optic nerve fibers
- Inner limiting membrane
- What are the functions of the Retinal pigment epithelium
- Absorbs light to prevent reflection and glare
- It is a component of the blood-retina barrier
- It restores photosensitivity to dissociated visual pigments
- It is responsible for the phagocytosis and disposal of membranous discs from rods and cones of the photoreceptor cells
- Name and classify the glands of the eyelids
- Merocrine glands
- Eccrine sweat glands
- Accessory lacrimal glands (glands of Wolfring and Krause)
- Holocrine glands
- Tarsal glands (Meibomian glands)
- Sebaceous glands of eyelashes (glands of Zeis)
- Apocrine glands
- Apocrine glands of the eyelashes (glands of Moll)
- Merocrine glands

