Table Of Contents
Acute Rhinosinusitis
Acute sinusitis is inflammation of the sinus cavities of the skull. Inflammation results in blockage, build-up of fluid, and pressure. It is most commonly viral. If symptoms last for more than 7-10 days it suggests a bacterial etiology, and antibiotics are indicated. The diagnosis of acute sinusitis is clinical.
| Etiology | Features |
|---|---|
| Acute viral rhinosinusitis | Self-limiting and resolves within 7 days. Nasal discharge and cough may last a further 3-4 days. |
| Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis | Discoloured mucus, severe local pain, Fever 38 C, Raised CRP/ESR, and ‘Double sickening’’ |
- Criteria for the diagnosis of acute sinusitis in adults Sudden onset of 2 or more symptoms for < 12 weeks
- Nasal blockage/obstruction/congestion OR nasal discharge (anterior or posterior drip)
- +/- Facial pain or pressure
- +/- Reduction or loss of smell
- Criteria for the diagnosis of acute sinusitis in children Sudden onset of 2 or more symptoms for < 12 weeks
- Nasal blockage/ obstruction/ congestion
- +/- Discoulored nasal discharge
- +/- Cough (daytime or night-time)
- Risk factors for Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis (DIIIMMES)
- Dental infection/procedure
- Iatrogenic (Sinus surgery, NG tube placement, Nasal packing)
- Impaired cilia motility: Cystic fibrosis, Kartegener syndrome
- Immunodeficiecy
- Mucosal oedema: Allergic rhinitis, URTI
- Mechanical obstruction: polyp, foreign body, tumor
- Environmental Factors e.g. Occupation
- Smoking
- Signs and symptoms
- Facial pain
- Dental and nasal pain (maxillary)
- Eye pain (ethmoidal)
- Frontal pain (frontal and sphenoidal)
- Fullness
- Purulent nasal discharge
- Headache
- Tooth pain
- Facial pain
- Physical exam
- Tenderness on palpation
- Tenderness on motion of the head
- Decreased transillumination
- Investigations
- Sinus CT: best initial test
- Sinus aspiration: most accurate test
- Indications for antibiotics in Acute Rhinosinusitis Antibiotics are reserved for Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis
- URTI symptoms worsen within 10 days after initial improvement (“Double sickening sign”)
- Signs and symptoms fail to resolve in 10 days
- Treatment
- Decongestants and nasal steroids e.g. Oxymetazoline and Mometasone for mild symptoms
- Antihistamines
- Analgesics e.g. Paracetamol and NSAIDS
- Nasal irrigation with saline
- Steam/heated humidified air +/- Eucalyptus, menthol
- Amoxicillin/clavulanate for Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis
- Complications
- Facial osteomyelitis (Pott’s puffy tumor)
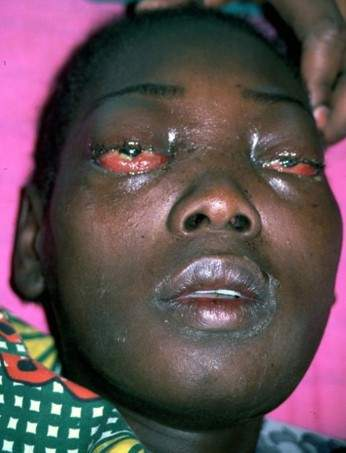
- Orbital cellulitis (ethmoidal sinusitis) → Blindness
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis (sphenoidal sinusitis): bilateral chemosis (edema of conjunctiva), proptosis, fixed orbit, and visual loss. Treatment ivolves broad spectrum IV antibiotics for 3-4 weeks
- Meningitis
- Brain/meningeal abscess
Chronic Bacterial Rhinosinusitis
Chronic Bacterial Rhinosinusitis results from untreated or inadequately treated acute (<4 weeks) or subacute (4 – 12 weeks) rhinosinusitis. It is considered if inflammation lasts for more than 12 weeks (3 months).
- Associated conditions
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Asthma
- Immunodeficiency
- Dental infections
- Poor mucociliary clearance: Kartegener syndrome, cystic fibrosis
- Granulomatous disease: Sarcoidosis
- GERD
- Obstructive sleep apnoea
- Signs and symptoms
- Chronic purulent discharge
- Less pain
- Physical examination
- Mucopurulent discharge
- Hypertrophied turbinates
- +/- polyps
- Investigations
- Nasal endoscopy
- CT paranasal sinuses: to determine the site of infection, for anatomic abnormalities or polyps
- Culture
- Treatment
- Intranasal steroids: 1st line treatmentAntibiotics for 2-6 weeksOral corticosteroids for 2-3 weeks for nasal polyposisFunctional endoscopic sinus surgery

