- Name the cell types of the olfactory epithelium and state their respective functions.
- Bipolar olfactory receptor cell – olfaction
- Supporting (sustentacular cells) – mechanical and metabolic support to receptor cells
- Basal cells – stem cells from which receptor and supporting cells regenerate
- Brush cells – general sensory cells
- What is the function of Bowman’s glands
- They secrete serous fluids that act as a solvent for odoriferous substances. Thus constant flow from the glands washes away old scents and allows new scents to be detected as they arise.
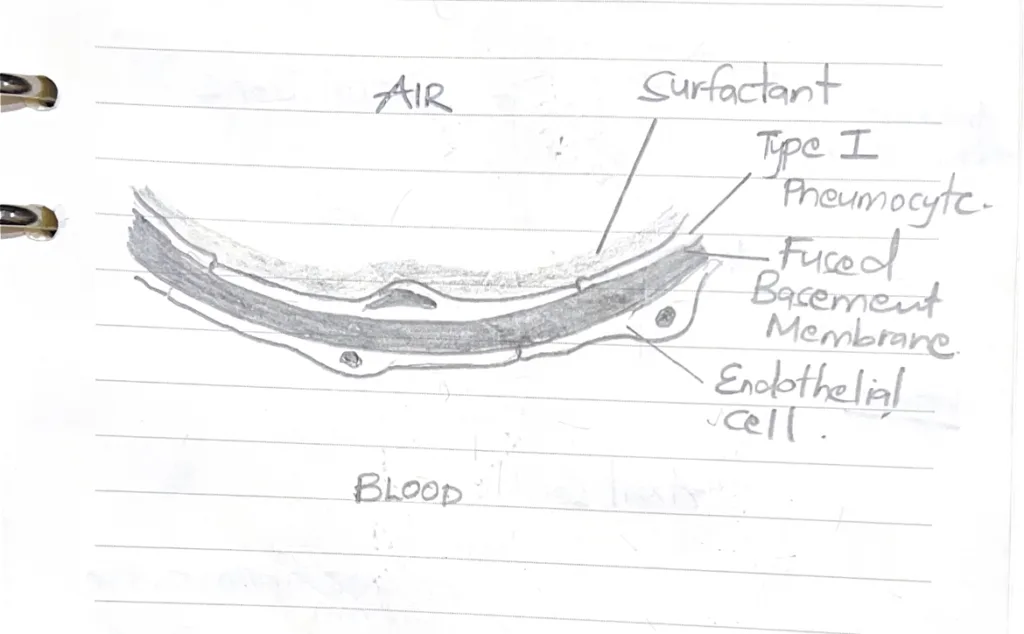
- What makes up the blood air barrier
- Surfactant
- Type I pneumocyte
- Fused basement membrane of Type I pneumocyte and endothelial cell
- Endothelial cell
- What is a bronchopulmonary/ mucociliary escalator It is the coordinated sweeping of the mucus coat by cilia towards the pharynx
- Describe the Proximal – distal changes in the respiratory tract
- Epithelium type: Simple Ciliated columnar cells → Simple squamous cells
- Goblet cells: Decrease in number up to the terminal bronchioles
- Ciliated cells: Reduce in number up to respiratory bronchioles. Are absent in alveoli
- Glands: Decrease in number up to respiratory bronchioles. Are absent in alveoli
- Hyaline cartilage: C-shaped rings in the extrapulmonary region. Disc shaped in the intrapulmonary region. Decrease in number proximo-distally. Absent in bronchiloes and alveoli
- Smooth muscles: Increase in number up to bronchioles. Absent in alveoli
- What is the function of Clara cells
- Secrete surface active agent that prevents luminal adhesion during airway collapse
- Produce Clara secretory protein (CC16), which is used as a measurable pulmonary marker in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and serum
- Bronchial levels of CC16 decrease in lung injury while serum levels increase
- Name the cell types of the respiratory mucosa and their respective functions
- Ciliated columnar epithelium: Mucociliary clearance
- Goblet cells: Mucous production
- Brush cells: Sensory
- Kultchitsky cells: Enteroendocrine
- Basal cells: Stem cells
- Clara cells: produce Clara cell secretory protein (CC16) and a surface active agent that prevents luminal adhesion should the airway collapse during expiration
- List the features of a bronchopulmonary segment
- Segmental bronchus
- A bronchial artery
- A pulmonary artery
- Veins and lymphatics draining along the periphery

