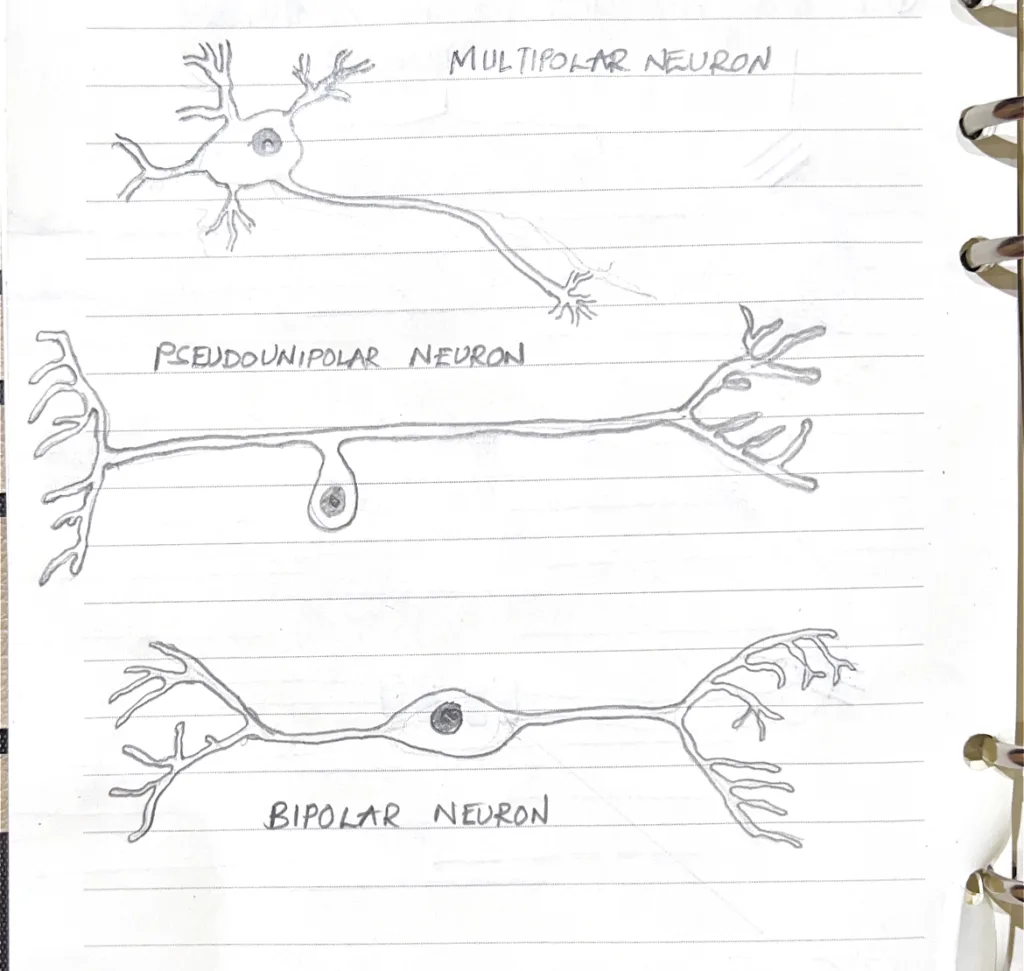
- Describe the classification of neurons based on shape. Give specific examples
- Multipolar neurons: One axon and two or more dendrites: Motor neurons, interneurons
- Bipolar neurons: One axon and one dendrite: Receptors for special senses (taste, smell, hearing, sight, equilibrium)
- Pseudounipolar (Unipolar) neurons: One axon that divides close to the cell bodies into two long axonal branches; one extends to the periphery while the other extends to the CNS: Sensory nerves of the dorsal root ganglia and cranial nerve ganglia
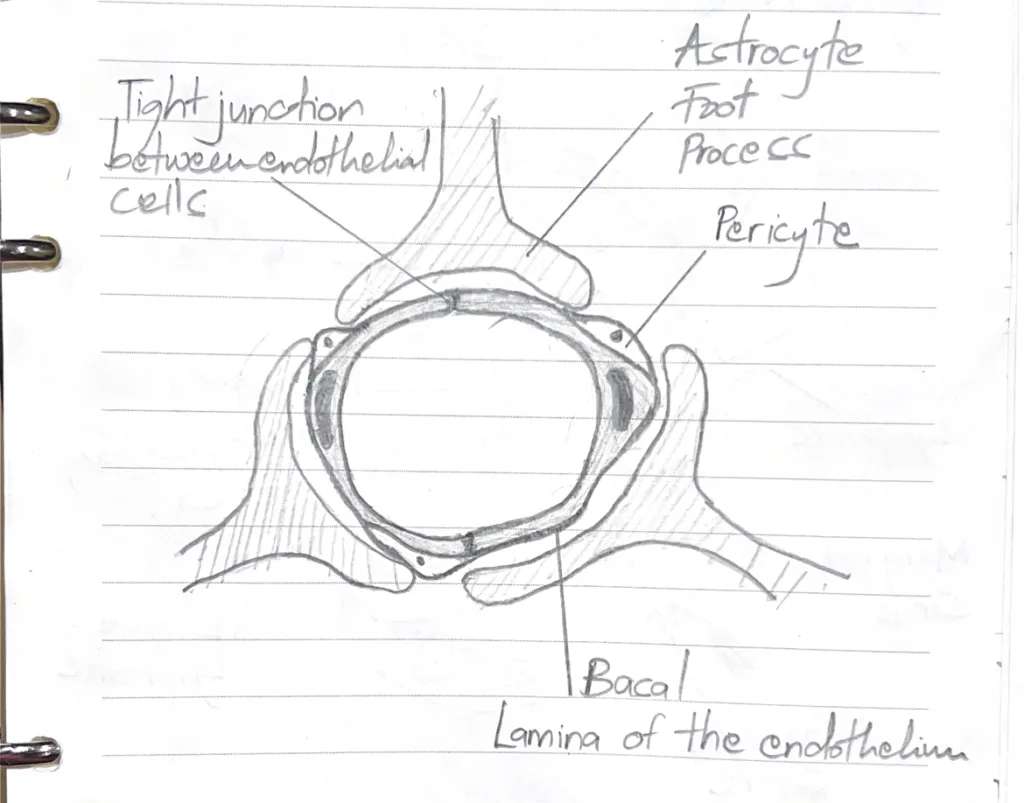
- What forms the blood brain barrier
- Tight junctions between endothelial cells
- PericytesBasal lamina of the endothelium
- Astrocyte foot processes
- List the examples of peripheral neuroglial cells
- Schwann cells
- Satellite cells
- Terminal neuroglia (teloglia: associated with the motor end plate)
- Enteric neuroglia (associated with the ganglia of the GIT)
- Muller’s cells (found in the retina)
- State examples of central neuroglial cells and state their respective functions
- Astrocytes: Support neurons physically and metabolically in the CNS
- Oligodendrocytes: Form and maintain myelin in the CNS
- Microglia: Phagocytes
- Ependymal cells: Produce CSF

