Abortion
Miscarriage (abortion) is defined as termination of pregnancy before 24 weeks gestation OR when fetal weight is estimated to be < 500g. The most common cause of pregnancy loss in the first trimester is fetal genetic abnormalities (aneuploidies e.g. Turner syndrome) while the most common cause of pregnancy loss in the second trimester are anatomic abnormalities of the uterus. A sterile speculum exam is important ****to assess the cervix, followed by a transvaginal or abdominal ultrasound to assess the viability of the fetus or a possible ectopic pregnancy.
Definition of terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Spontaneous abotion (miscarriage) | Involuntary pregnancy loss before viability (WHO 20 weeks gestation or loss of a fetus weighing less than 500 g) |
| Septic abortion | Miscarriage complicated by uterine infection |
| Stillbirth | Pregnancy loss after viability (WHO 20 weeks gestation or fetus > 500 g ) |
| Recurrent pregnancy losses | Spontaneous loss of > 2 pregnancies. Affects 1% of couples. Causes (anatomic defects), hormonal – corpus luteum insufficiency, TORCH complex |
| Second-trimester pregnancy loss | Pregnancy loss between 13 0/7 – 19 6/7 |
| Stillbirth or fetal death | Pregnancy loss > 24 0/7 gestational age or at weight >500g |
| Blighted ovum | Anembryonic pregnancy |
- Causes of spontaneous abortion
- Fetal chromosomal abnormalities (50%): most common cause
- Turner’s syndrome (Monosomy 45, X)
- Klinefelters syndrome (Trisomy XXY)
- Polyploidy
- Fetal gross abnormalities
- Neural tube defects (NTDs)
- Anencephaly
- Anatomical factors: pregnancy loss > 14 weeks
- Cervical incompetence – miscarriages with reduced gestation age since cervix becomes weaker with each pregnancy
- Mullerian fusion abnormalities (bicornuate or unicornuate uterus, septae) – pregnancy loss with increasing gestational age
- Fibroids – pregnancy loss with increasing gestational age
- Corpus luteum insufficiency: inadequate production of progesterone and estrogen before 12 weeks
- Inadequate endometrial preparation
- Inadequate pregnancy support
- Maternal chronic disease: associated with recurrent pregnancy loss
- Hyperthyroidism
- Diabetes mellitus
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
- Thromophilias
- Maternal Infection
- TORCH complex (Toxoplasma, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, Hepatitis B, Herpes Simplex II, Syphillis)
- Malaria
- Listeria monocytogens
- Mycoplasma
- Immunologic disorders: may lead to inability to conceive in addition to recurrent pregnancy losses
- Blood group incompatibility
- Environmental factors
- Cigarette smoking
- Alcohol
- Exposure to certain chemicals, radiation and embryotoxic agents (mifepristone, methotrexate)
- Trauma
- Direct or indirect
- Blunt or sharp
- Idiopathic
- Fetal chromosomal abnormalities (50%): most common cause
- Pathophysiology
- Hemorrhage into the decidua basalis causes necrotic changes and fetal demise
- Rupture of membrnaes if > 14 weeks gestation
- Associated with uterine contractions and cervical dilation
- How do anatomical anomalies cause miscarriage?
- Reduced intrauterine volume
- Reduced compliance of myometriam
- Inadequate endometrial preparation for imlpantation
- Reduced expansile property
- Reduced placental vascularity( when implanted on septum)
- Increased uterine irritability and contractility
- Signs and symptoms of abortion
- Bleeding per vagina
- Lower abdominal pain
- Investigations
- Pelvic examination (including speculum)
- Pelvic ultrasound: to confirm viability
- Complete blood count: for anaemia and leukocystosis in case of sepsis
- Blood group and cross match: significant bleeding may require transfusion. Determine Rh status ****
Types of Abortion
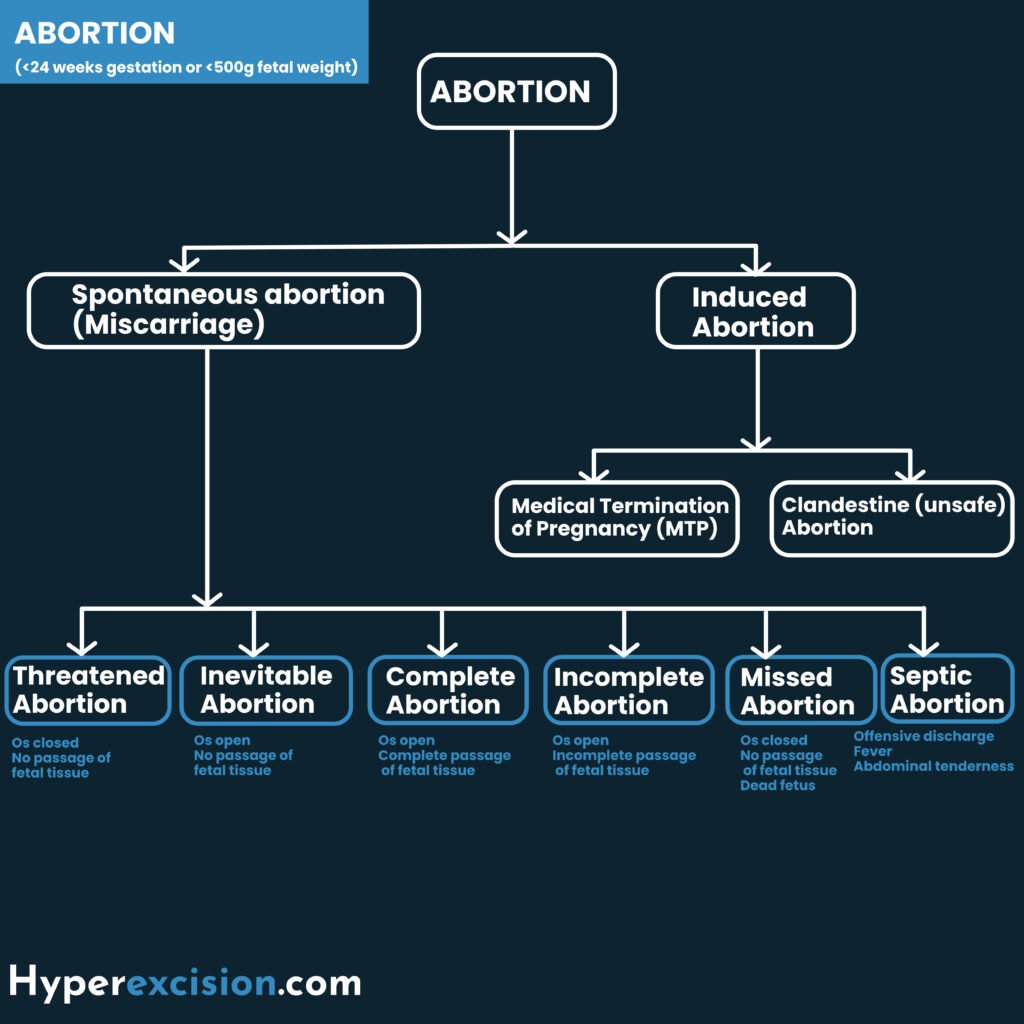
Types of Abortion
| Type of abortion based on stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Threatened abortion | Vaginal bleeding before 24 weeks gestational age in the setting of a positive urine and/or blood pregnancy test with a closed cervical os, no LAPs, without passage of products of conception, and no evidence of fetal demise. About 50% of threatened miscarriange proceed to miscarriage. A threatened miscarriage can either progress into a complete miscarriage or go on to have a normal pregnancy. Others will have incomplete miscarriages with retained products of conception (RPOCs) leading to bleeding, shock, and sepsis. |
| Inevitable abortion | Bleeding with an open cervical os, no passage of fetal tissue |
| Incomplete abortion | Bleeding with an open cervical os with passage of some but not all fetal tissue |
| Complete abortion | Bleeding with a closed cervical os, all fetal tissue has passed, and the uterus empty |
| Missed abortion | No bleeding with a closed cervical os, the fetus is dead, POCs in utero. Uterus size < gestational age. |
Ultrasound findings, clinical features and management of the different types of abortion
| Type of abortion | Ultrasound finding | Clinical features | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threatened abortion | Intrauterine pregnancy with fetal heart beat | minimal vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain, os closed, uterine size equivalent to gestational age | Supportive, bed rest, progesterone |
| Missed abortion | Intrauterine pregnancy with no fetal heart beat. Blighted ovum (unembryonic collapse) | Asymptomatic (diagnosed at booking ultrasound). Irregular dark bleeding and regression of signs and symptoms of pregnancy. | Medical or surgical evacuation |
| Inevitable abortion | Intrauterine pregnancy with no fetal cardiac activity | Vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain, os open, uterine size equivalent to gestational age | > 14 weeks without bleeding allow to progress with augmentation with oxytocin, < 14 weeks |
| Incomplete abortion | Retained products of conception | Vaginal bleeding in lumps and abdominal pain, os open and products of conception located in the cervical os | Remove tissue at time of speculum if possible, uterine evacuation, treatment of shock and hemorrhage (can lead to exsanguination), antibiotics, analgesics |
| Complete abortion | Empty uterus (serum hCG to exclude ectopic pregnancy) | No LAPs, Pain and bleeding resolved, cervical os closed, uterine size < gestational age, post-abortion lochia | Supportive (ergometrine and antibiotics) |
Cervical os findings for the different types of miscarriage
| Cervical os closed | Cervical os open | |
|---|---|---|
| No passage of fetal tissue | Threatened miscarriage | Inevitable miscarriage |
| Fetal tissue passed | Complete miscarriage | Incomplete miscarriage |
| Feature | Diagnosis |
|---|---|
| No BLEED + NO passage of fetal tissue + Dead fetus on ultrasound | Missed miscarriage |
Incomplete vs threatened miscarriage
| Incomplete abortion | Threatened abortion | |
|---|---|---|
| Bleeding | Slight to heavy | Slight to moderate |
| Cervical os | open | closed |
| Uterine size | Less than or equal to the Gestation date | Equal to gestation date |
| Uterus | Tender or firm | Soft |
Threatened Abortion
A threatened abortion presents as vaginal bleeding before 24 weeks gestational age in the setting of a positive urine and/or blood pregnancy test with a closed cervical os, no lower abdominal pain, without passage of products of conception, and no evidence of fetal demise. About 50% of threatened miscarriange proceed to miscarriage. A threatened miscarriage can either progress into a complete miscarriage or go on to have a normal pregnancy. Others will have incomplete miscarriages with retained products of conception (RPOCs) leading to bleeding, shock, and sepsis.
- Indications for admission in threatened abortion
- Excessive bleeding
- GBD > 14 weeks
- Bad obstetric history
- Lives far away and cannot get help if the bleeding gets worse
- Treatment of Threatened abortion
- Admit if indicated
- Avoid heavy activity
- Pelvic rest
- Follow-up with repeat ultrasound and b-hCG in 7-10 days (expect it to rise and progress)
- RhoGAM if rhesus negative (to prevent alloimmunization)
- Progesterone e.g. dydrogesterone (duphastone
- Pain management
Complete abortion
A complete abortion presents as per vaginal bleeding with a closed cervical os. All fetal tissue has passed and the uterus is empty.
- Treatment of Complete miscarriage ****
- No further management is needed; reassurance and supportive managementt
- Initiate Post-abortion care, including RhoGAM if Rh negative
Inevitable, Incomplete and Missed abortion
- Signs and symptoms of retained products of conception
- Heavy bleeding (greater than menses)
- Prolonged bleeding (over three weeks)
- Fever
- Lower abdominal pain that is worsening or cannot be controlled by analgesics
- Uterine tenderness
- Indications for evacuation of uterine contents
- Considerable bleeding (requires urgent evacuation)
- Bleeding more than during menstruation, which continues >24h
- Retained products of conception on speculum exam or ultrasound
- Infection (septic abortion)
- Physical interference with the pregnancy
- Treatment of Inevitable miscarriage, incomplete miscarriage, missed miscarriage
- Manage expectantly OR
- Medical evacuation using Misoprostol or Oxytocin or Ergometrine
- Surgical evacuation using Manual Vacuum aspiration (< 14 weeks) or Dilation and Curretage (D&C)
- Follow-up with repeat sonogram and B-hCG in 4-7 days
- RhoGAM if rhesus negative
Septic abortion
A septic abortion is a miscarriage that is complicated by severe uterine infection (endometritis, parametritis) that progresses to a generalized infection. Gram negative and positive, aerobes and anaerobes
- Common infectious organisms in septic abortion
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococci
- Bacteroides fragilis
- Clostridium perfringens or welchi
- Signs and Symptoms of septic abortion
- Passage of foul-smelling POCs
- Offensive discharge per vagina
- Tachycardia
- Pyrexia
- Uterine, adnexal, and peritoneal tenderness
- Acute kidney injury
- Endotoxic shock
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- Treatment
- ABCs
- Fluid resuscitation and vasopressors if septic shock
- IV Metronidazole + Doxycycline + Ceftriaxone
- Evacuate uterine contents (source controle)
Induced abortion
An induced abortion is an intended termination of pregnancy. It can be therapeutic (of medical benefit to the mother) or Criminal (of no medical benefit, contravenes the law)
Types of induced abortion
| Type of abortion | Description |
|---|---|
| Therapeutic abortion | For medical benefit to the mother or fetal abnormality (missed abortion) |
| Criminal abortion | No medical benefit to the mother. Goes against the law |
| Clandestine abortion | Unprofessionaly done in an inappropriate environment |
| Legal abortion | Done when the life of the mother is in danger |
- Termination of pregnancy in the first trimester
- Mifepristone (RU486)
- Mifepristone + Misoprostol
- Methotrexate (in very early pregnancy)
- Manual vaccum aspiration
- Dilation and Curretage
- Termination of pregnancy in the second trimester
- Prostaglandins (extra-amniotic, intra-amniotic or pessaries/gel) for cervical ripening and induction
- Oxytocin > 14 weeks after cervical ripening
- Hysterotomy > 14 weeks for women with previous uterine scars
Manual Vaccum Aspiration (MVA)
MVA uses a vacuum to evacuate the contents of the uterus.
- Indications for MVA
- Incomplete miscarriage < 13 weeks LMP (12 weeks uterine size)
- Termination of pregnancy < 13 weeks LMP (12 weeks uterine size)
- Molar pregnancy
- Early complications of MVA
- Incomplete evacuation
- Perforated uterus → bleeding → pelvic infection
- Complications of anaesthesia
- Haematometra (retention of blood in the uterine cavity)
- Late complications of MVA
- Asherman’s syndrome
- Infertility
Post-abortion care
- Post-abortion care (PAC)
- Monitor vitals for hemodynamic stability and manage ****any complications that may arise
- Pain management with NSAIDs and Acetaminophen. Opioids are rarely needed.
- Rh Immunoglobulin if Rhesus negative
- Contraceptives can be started on the same day. Ovulation may resume as early as 2 weeks post-abortion.
- Psychological support and counselling. Screen for depression, PTSD, or guilt (especially in induced abortion
- Consider low-dose aspirin and progesterone supplementation for subsequent pregnancy
Complications of Early Pregnancy Loss
- Acute complications
- Long term complications
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Infertility
- Asherman syndrome
- Socioeconomic complications
- Marital disharmony
- Stigmatization
- The cost of treatment is expensive
Complications of early pregnancy loss
| Complication | Signs/Symptoms | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Hemorrhage | Heavy bleeding, hypotension | Misoprostol, uterine massage, evacuation if RPOC |
| Infection | Fever, foul discharge, cervical motion tenderness | Doxycycline + Metronidazole |
| RPOC | Persistent bleeding, clots | Repeat evacuation or misoprostol |
| Uterine perforation | Severe pain, abdominal distension | Laparoscopy/laparotomy (rare, <0.1%) |
Further Reading
Manual Vacuum Aspiration – https://medicalguidelines.msf.org/en/viewport/ONC/english/9-5-manual-vacuum-aspiration-mva-51417954.html

