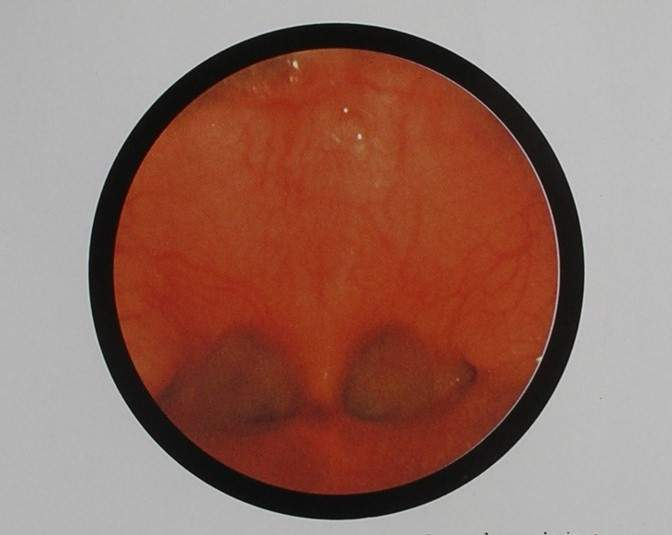
Choanal atresia is a congenital defect in which the openings that connect the nasal cavity to the nasopharynx (choanae) are occluded, either by soft tissue, bone, or both. (90% bony, 10% membranous and 5% mixed)
It is more common in females. Most cases are unilateral (65%, right-side predominance). It is associated with prenatal use of carbimazole and methimazole, cigarette smoking, caffeine (> 3 cups a day), and elevated vitamin B12, vitamin B3 and zinc levels.
- Pathophysiology
- Persistence of the bucconasal membrane or Abnormal migration of neural crest cells into the nasal vault
- Results in complete bony (30%), mixed bony-membranous (70%), or membranous (rare) obstruction of the posterior nasal cavity
- The bony components are from the pterygoid plate and vomer
- What are the theories behind the development of choanal atresia?
- Persistence of buccopharyngeal membrane during the embryonic period
- Persistence of the oronasal membrane beyond the embryonic period
- Outgrowth of the palatine bone
- Abnormal persistence of the mesoderm leading to atypical mesodermal adhesions
- Incomplete mesodermal resorption
- Altered local growth factors
- Abnormal neural crest cell migration
- Signs and symptoms
- Unilateral: may be asymptomatic
- Rhinorrhoea
- Nasal obstruction
- Bilateral
- Cycles of apnoea and cyanosis followed by crying (neonates are obligate nose breathers)
- Blue baby (central cyanosis)
- Color relieved when the neonate cries and worsens when feeding
- Unilateral: may be asymptomatic
- Investigations and bedside tests
- Cotton wisp test
- Metallic spatula test/ mirror test to detect condensation
- Attempt transnasal passage of a 6 Fr catheter
- Put blue dye through nostril
- Attempt nose blowing with an occluded nostril
- Nasal endoscopy
- CT scan
- EKG
- Associated syndromes
- CHARGE syndrome (most common concurrent syndrome with bilateral atresia in 50%)
- Coloboma Idris
- Heart Defects
- Atresia (Choanal)
- Retardation (Mental)
- Genital Hypoplasia
- Ear defects
- Apert, Treacher Collins, Crouzon, Trisomy 21, and 22q11 deletion
- CHARGE syndrome (most common concurrent syndrome with bilateral atresia in 50%)
- Treatment of bilateral atresia
- Establish an oral airway with McGovern Airway (cut the end of a bottle nipple and secure it around the mouth) or Oropharyngeal airway. Intubation is rarely required
- Feeding through an orogastric tube
- Oxygen supplementation using a mask
- Arrange for repair as early as possible
- Treatment of unilateral atresia
- Repair electively
- Repair options
- Surgical repair via Transnasal, Transantral, Transseptal, or Transpalatal approach → drill + stent
- The transnasal approach is usually endoscopic
- Transantral approach can create a large cavity for recurrent cases
- The transpalatal approach is a classical approach that may disrupt orthodontic growth
- Surgical repair via Transnasal, Transantral, Transseptal, or Transpalatal approach → drill + stent