Overview
Pregnancy is the state of having products of conception in the uterus or elsewhere, be it normally or abnormally. Amenorrhea is the most common presentation of pregnancy.
- Intrauterine pregnancy
- Most common result of fertilization
- Consistent with viable childbirth
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Products of conception a implanted outside the uterus
- Molar pregnancy
- Non-viable pregnant state with abnormal products of conception due to genetic anomaly. A product of “how the egg was fertilized” or the “state of the egg during fertilization (e.g. empty egg). Results in Gestational Trophoblastic Disease.
- Presentation of pregnancy
- Symptoms
- Amenorrhoea (Amenorrhea is the most common presentation of pregnancy)
- Nausea/Vomiting
- Breast tenderness and swelling
- Quickening (fetal movement felt during the first few months into pregnancy)
- Signs
- Chadwick sign (Bluish discoloration of the vagina/cervix 4 weeks after LNMP, 2 weeks after conception)
- Softening and cyanosis of the cervix
- Ladin’s sign (Softening of the uterus at 6 weeks gestation)
- Linea nigra (3/4 of pregnant women 20-22 weeks LNMP coz placenta makes MSH)
- Telangiectasias
- Palmar erythema
- Symptoms
Diagnosing pregnancy
Urine qualitative B-hCG is the best initial test for diagnosing and ruling out pregnancy. Serum quantitative-hCG is even better. A positive pregnancy test is followed up by an abdominopelvic ultrasound.
- Why is sonography done after positive clinical hCG
- To confirm pregnancy
- To locate the gestational sac (should hopefully be in the uterus)
- How early can the gestational sac be detected by ultrasound?
- As early as 5 weeks LNMP
- How early can fetal heart motion be visualized by ultrasound?
- As early as 6 weeks LNMP
- How early can fetal heart sounds be heard?
- Towards the end of the first trimester
Quantitative Human chorionic gonadotropin
Inaccurate dating is the most common cause of abnormal quantitative hCG.
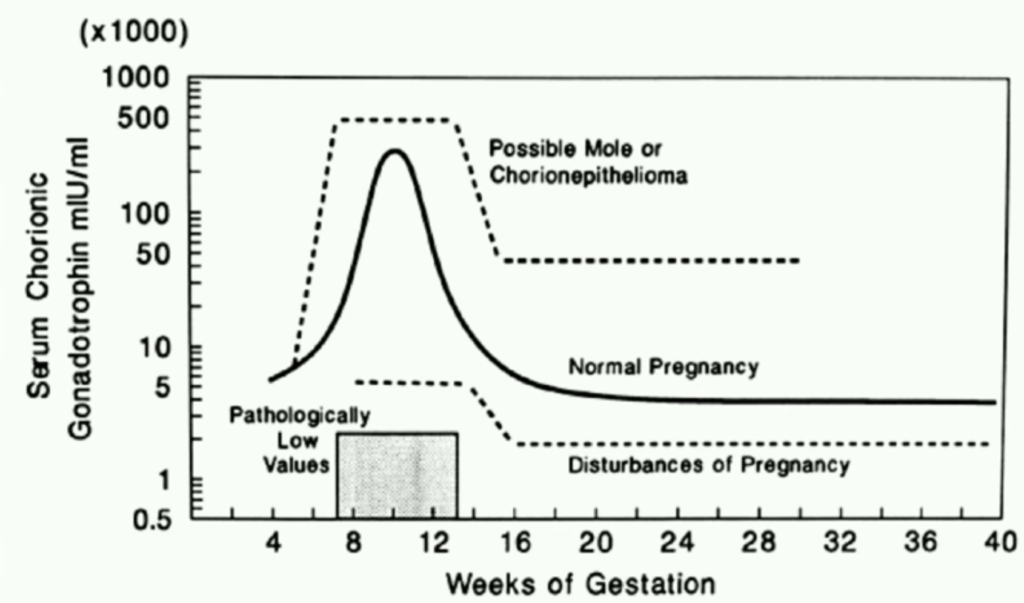
- Causes of low quantitative hCG
- Inaccurate dating
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Threatened abortion
- Missed abortion
- Causes of high quantitative hCG
- Inaccurate dating
- Multiple gestations
- Molar pregnancy
- Choriocarcinoma
- Embryonal carcinoma
Dating the pregnancy
Pregnancy is dated from the beginning of the first day of the cycle during which the woman becomes pregnant ORthe date of the last menstrual period (LMP), The most accurate means of determining the Estimated Date of Confinement (EDC) is the first-trimester ultrasound.
| Event | Corresponding Gestation By Date |
|---|---|
| Ovulation | 2 weeks LMP (28-day cycle), 1 weeks LMP (21-day cycle), 3 weeks LMP (35-day cycle) |
| Conception | 2 weeks LMP |
| Implantation | 3 weeks LMP |
| 1st positive B-hCG | 3 weeks LMP (1 week after conception) |
| Typically discovers pregnancy | 4 – 5 weeks LMP (after missing her normal period) |
Naegele’s Rule for calculating the Estimated Date of Delivery
Naegele’s rule is used to determine the due date. Subtract 3 months from the LNMP and add 7 days and 1 year(assuming a 28-day cycle)
- What is the due date for LMP: 19/12/2022
- 26/09/2023
Cycle length
The follicular phase varies. The luteal phase is fixed/constant at around 14 days.
| Cycle length | Follicular phase length |
|---|---|
| 28 day cycle | 14 days |
| 21 day cycle | 7 days |
| 35 day cycle | 21 days |
Useful terms
Gravidity
Gravidity is the state of being pregnant
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Gravida | A woman who is pregnant |
| Nulligravida | A woman who has never been pregnant |
| Primigravida | A woman who is in her first pregnancy |
| Multigravida | A woman who has had two or more pregnancies |
Parity
Parity is the number of pregnancies in which the fetus(es) have reached the point of viability (normally assigned 20 weeks)
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Nullipara | A woman who has never completed a pregnancy beyond the state of fetal viability |
| Primipara | A woman who has completed one pregnancy beyond the stage of fetal viability |
| Multipara | A woman who has completed multiple pregnancies beyond the stage of fetal viability |
Term
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Preterm | A pregnancy that has reached 20 weeks LMP but before 37 weeks LMP |
| Term | A pregnancy from 37 weeks LMP to 42 weeks LMP |
| Early Term | A pregnancy from 37 0/7 to 37 6/7 weeks LMP |
| Full Term | A pregnancy from 38 0/7 to 40 6/7 weeks LMP |
| Late Term | A pregnancy from 41 0/7 to 41 6/7 weeks LMP |
| Post Term | A pregnancy after 42 weeks LMP |
| Miscarriage/Abortion | Delivery of a dead fetus(es) before 20 weeks LMP |
| Stillbirth | Delivery of a dead fetus(es) after 20 weeks LMP |
GPA System
- G (gravida)
- Total number of known pregnancies the woman has had, including the current ne, regardless of outcome
- P (para)
- Total number of pregnancies the woman has had that led to a birth of an infant after 20 weeks LMP OR greater than 500g
- Multiple gestations are considered one pregnancy
- A (abortus)
- Number of pregnancies that resulted in spontaneous or induced abortions
- Abortus = delivery of a dead fetus(es) before 20 weeks LMP
- Number of pregnancies that resulted in spontaneous or induced abortions
- A woman is on her 4th pregnancy. Has previously delivered one live singleton at 40w0d, one live singleton at 35w5d, and one live set of twins at 34w7d.
- G4 P3 A0 or
- G4 P3+0
G/TPAL system
- G (gravida)
- Total number of known pregnancies the woman has had. Including the current one. Regardless of the outcome.
- Multiple gestations count as one pregnancy
- T (term)
- Number of pregnancies that result in a term delivery.
- Term is considered delivery after 37 weeks.
- P (preterm)
- Number of pregnancies that resulted in a preterm delivery
- A (abortus)
- Number of pregnancies that resulted in spontaneous or induced abortions
- L (living)
- Number of live infants born (babies that were alive coming out)
- A woman is on her 4th pregnancy. Has previously delivered one live singleton at 40w0d, one live singleton at 35w5d, and one live set of twins at 34w7d.
- G4 T1 P2 A0 L4 or
- G4 1204
Practice Questions
- Shiru is 8 weeks pregnant. It is her first known pregnancy.
- G1 P0+0
- G1 P0 A0
- G1 T0 P0 A0 L0 (G1 0000)
- Shiru later gives birth to a live boy at 40 weeks gestation via spontaneous vertex delivery
- Now P1+0
- G1 P1 A0
- G1 T1 P0 A0 L1 (G1 1001)
- Karimi has just given birth to a live girl at 32 weeks gestation via cesarean delivery. It was her first known pregnancy.
- Now P1+0
- G1 P1 A0
- G1 T0 P1 A0 L1 (G1 0101)
- Moraa is 15 weeks pregnant. It is her third known pregnancy. Her first pregnancy resulted in a spontaneous vertex delivery at 39 weeks and her second pregnancy was a Caesarean at 40 weeks.
- G3 P2+0
- G3 P2 A0
- G3 T2 P0 A0 L2 (G3 2002)
- Tandi is 26 weeks pregnant. It is her fourth known pregnancy. Her first pregnancy ended in a miscarriage at 10 weeks. The second resulted in a spontaneous vertex delivery of live twin boys at 38 weeks. The third resulted in a spontaneous vertex delivery of a live girl at 35 weeks.
- G4 P2+1
- G4 P2 A1
- G4 T1 P1 A1 L3 (G4 1113)
- Aysha gave birth to a live girl at 39 weeks, live twin boys at 34 weeks, had a miscarriage at 8 weeks, then a live boy at 31 weeks. She is now pregnant.
- G4 P3+1
- G5 P3 A1
- G5 T2 P1 A1 L4 (G5 2114)
- Agutu presents to the clinic and is confirmed to have an intrauterine pregnancy via ultrasound. She says that her last day of bleeding was 9/7/2022. She has regular 28-day periods. She wants to know her due date.
- Estimated Date of Delivery: 16/4/2023
