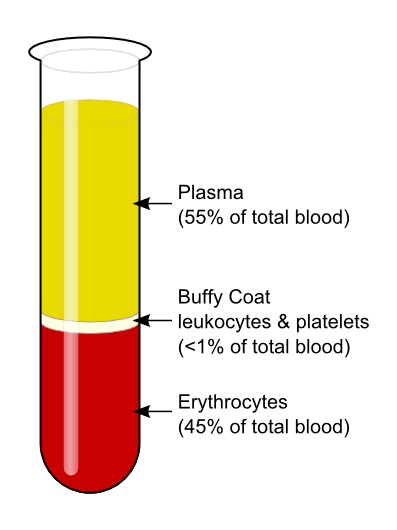
Centrifugation
- Preparation of a buffy coat
- 2 glass test tubes are filled with EDTA anticoagulated blood
- The test tubes are centrifuged at RCF 1000g for 15 minutes
- The supernatant plasma above the buffy coat is removed and discarded
- The buffy coat layer, red cells immediately below, and small amount of supernatant plasma are transferred on a slide and mixed using an applicator stick
- A thin preparation is made
- The preparation is air-dry
- Once dry it is fixed with alcohol for 2 minutes
- The slide is then stained using Giemsa staining method
- The preparation is observed at 40X objective and under oil immersion at 100X
- Uses of a buffy coat preparation
- DNA isolation from blood samples
- Purification of large amounts of DNA from relatively small sample sizes
- Differential counting of white blood cells
- Quantitative Buffy coat (QBC) to detect blood parasites: plasmosium spp, Leishmania donovani, trypanosomes, microfilariae and Histoplasma capsulatum infection
| Serum | Plasma | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Liquid that remains after blood has clotted | Liquid that remains when clotting is prevented |
| Preparation | Centrifuge clotted blood | Centrifuge whole blood with anticoagulant |
| Fibrinogen | Absent | Present |
Complete Blood Count

- Components and utility of a complete blood count
- Components
- Total WBC count
- WBC differential count
- Total RBC count
- Hematocrit
- Hemoglobin
- Red cell indices (MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW)
- Total platelet count
- Platelet indices (MPV, PDW)
- Uses
- Diagnosis of anemia
- Diagnosis of myeloproliferative disorders
- Diagnosis of platelet abnormalities
- Components
- Principles employed by a coulter counter
- Electrical impedance
- Photometry
- Light scatter
Peripheral blood film
A PBF is a thin layer of blood smeared on a glass slide and stained to allow microscopic examination of blood cells
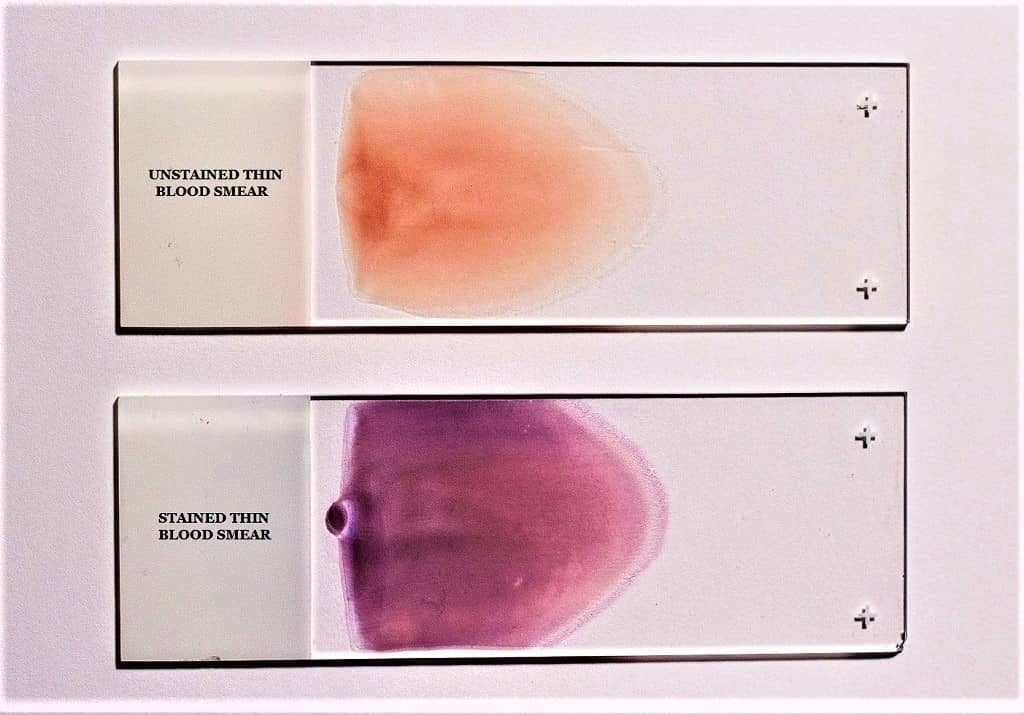
- Preparation ****
- Blood is spread on a glass slide
- Air dried on the glass slide
- Stained using a Romanowsky stain i.e. Leishman stain
- Clinical utility of a peripheral blood film
- Morphological classification of Anaemia
- Screening and diagnosis of malignancies with possible bon
- Screening and diagnosis of acute and chronic myeloproliferative diseases
- Diagnosis of infection
- Evaluation of therapeutic response to RBC and WBC disorders
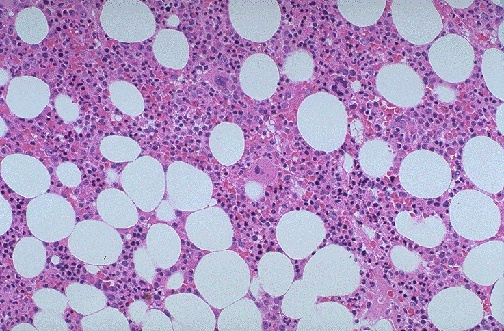
Bone Marrow Aspirate
A bone marrow aspirate is a procedure used to aspirate the cellular components, tissue fragments, or both, from a bone marrow for cytological assessment and analysis directed toward assessing the morphology and obtaining a differential cell count.
- Sites
- PSIS, ASIS, Sternum, Anterior tibia of neonate
- Procedure
- Site is prepared with antiseptic
- The skin and underlying tissue to the periosteum is infiltrated with a local anesthetic
- A skin incision is made with a surgical blade
- A bone marrow aspiration, with a stylet locked in place, needle is passed through the incision
- Once it contacts bone it is rotated clockwise and counter clockwise until it penetrated into the marrow cavity
- A 2mL syringe is used to aspirate approximately 0.3mL of bone marrow
- Slide preparation
- Squash preparation
- Stains
- Wright and May-Grunwald-Giemsa stains
- Prussian blue for iron study
- Myeloperoxidase, Sudan Black B and LAP for AML
- PAS for glycogen storage diseases
- Clinical Utility of Bone Marrow Aspirate
- Diagnosis, staging and monitoring of lymphoproliferative disorders
- Evaluation of cytopenia, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, anaemia and iron status
- Rule out infiltrative infectious disease (fungal infections, tuberculosis and other granulomatoses
- Diagnosis of storage diseases (Niemann-Pick disease and Gaucher disease)
- Assessment of metastatic carcinoma and granulomatous disease (Sarcoidosis)
- Reveal toxic effects of certain offending medications or substances e.g. alcohol or nutritional deficiencies e.g. copper, zinc, B12, folate
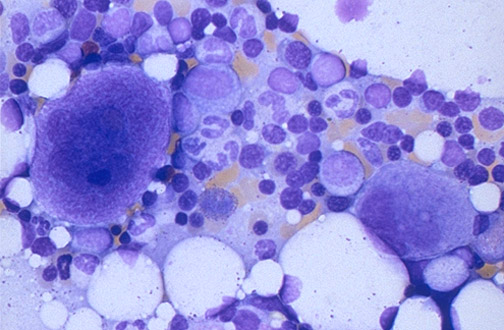

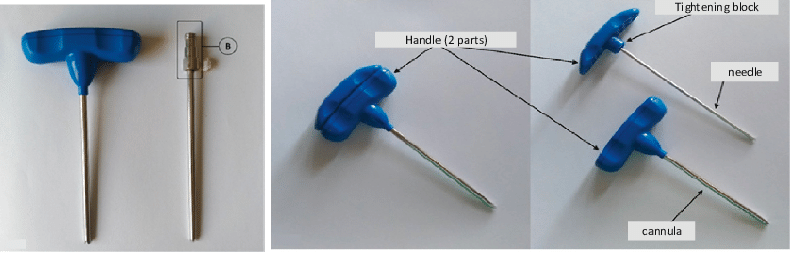
Trephine Biopsy
A biopsy of bone marrow yielding a cylindrical-shaped solid piece of BM
- Sites
- PSIS
- ASIS
- Sternum
- Anterior tibia of neonate
- Procedure
- Site is prepared with antiseptic
- The skin and underlying tissue to the periosteum is infiltrated with a local anaesthetic
- A skin incision is made with a surgical blade
- A trephine needle is advanced with a twisting motion and rotated to obtain a solid piece of bone marrow
- Slide preparation
- Squash preparation
- Stains
- Wright and May-Grunwald-Giemsa stains
- Prussian blue for iron study
- Myeloperoxidase, Sudan Black B and LAP for AML
- PAS for glycogen storage diseases
- Clinical utility of bone marrow biopsy
- Diagnosis staging and monitoring of lymphoproliferative disorders
- Evaluation of cytopenia, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis , anemia and iron status
- Rule out infiltrative infectious disease (fungal infections, tuberculosis and other granulomatoses
- Diagnosis of storage diseases (Niemann-Pick disease and Gaucher disease)
- Assessment of metastatic carcinoma and granulomatous disease (Sarcoidosis)
- Reveal toxic effects of certain offending medications or substances e.g. alcohol or nutritional deficiencies e.g. copper, zinc, B12, folate
- Components of bone marrow micro-environment and their role in hematopoiesis
- Bone marrow stroma
- Allows attachment of Stem Cells
- Contributes signals controlling proliferation and differentiation
- Regulates HSC localization, facilitating interaction with stromal cells
- fibronectin, laminin, collagen
- Bone marrow stromal cells
- Physical support for HSCs
- Produce growth factors and cell surface proteins that influence differentiation
- Regulate hemopoiesis via direct contact and soluble mediators (adhesive ligands, synthesis of ECM, production of signaling molecules, cytokines)
- Fibroblast, osteoblast (maintain HSC in a quiescent state), macrophage (Phagocytosis), endothelial cells, adipocytes, mesenchymal stem cells (0.01% diff to mesenchymal tissue)
- Bone marrow stroma