Cervical cysts
Cervical cysts need not be removed unless they are symptomatic or interfere with pap testing.
| Benign lesion | Description |
|---|---|
| Nabothian cyst | Clear to yellow-white elevations of the endocervix or proximal ectocervix. Contain mucus. No more than 1 cm in diameter. Most common cyst |
| Mesonephric cyst | Remnants of the Wolffian duct. Extend deeper into the cervical stoma. Commonly found in the ectocervix. Cervical equivalent to Gardner cysts. |
| Endometriosis | Red-purple in appearance. Associated sx worsen within days of menstruation |

Cervical polyps
These are asymptomatic and almost always benign. Usually incidental findings on cervical exam are performed for other purposes. Appears as a sessile/pedunculated mass. Tx involves removal since bleeding from polyps can mask other sources of bleeding d/t more problematic causes (e.g. cervical ca, fibroids, adenomyosis, endometrial polyps, endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial cancer).
- Signs and symptom
- Postcoital bleeding
- Intermenstrual bleeding
- Treatment
- Polypectomy
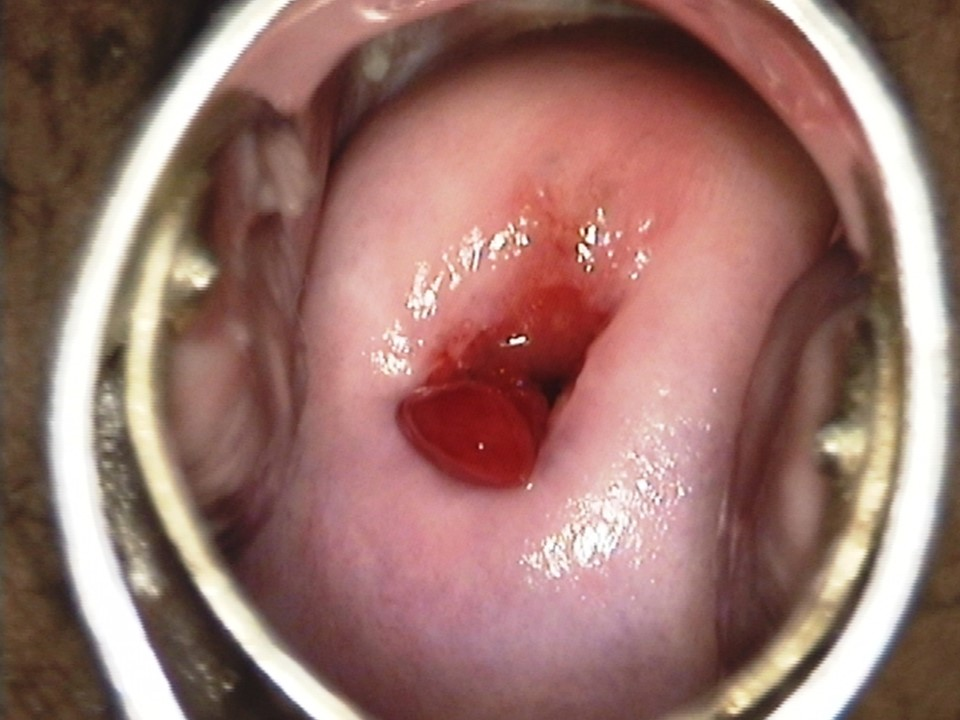
Cervical fibroids
Leiomyomas found in the cervix. Symptoms depend on size. Can be confused with cervical ca.
- Signs and symptoms
- Intemenstrual bleeding
- Dyspareunia
- Bladder/rectal pressure
- Ostetric complications
- Treatment
- Screen for cervical cancer
- Monitor w/regular gynecologic visits
- Elective removal if symptomatic
Cervical stenosis
Cervical stenosis is a narrowing or obliteration of the cervical canal. May be congenital or acquired. Mild cervical stenosis is usually asymptomatic. The inability to pass a 1 – 2 mm probe into the uterine cavity is diagnostic for cervical stenosis.
- Congenital causes
- Segmental Mullerian hypoplasia (cf. vaginal atresia)
- Acquired causes
- Trauma (OB)
- Post-op (s/p LEEP, conization, D&C)
- Infection
- Radiation
- Atrophy
- Signs and symptoms
- Cryptomenorrhoea
- Secondary dysmenorrhea
- Infertility
- Obstetric complications
- Treatment
- Cervical dilation

