Overview
- Investigations for vaginal discharge/irritation
- Speculum exam
- Vaginal swab
- Vaginal pH
- Vaginal KOH prep
- Wet mount (of vaginal secretions)
- Whiff test
- NAAT for chlamydia and gonorrhea
| Trichomoniasis | Candida vaginitis | Bacterial vaginosis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Exam | Erythema and irritation | Erythema and irritation | Unremarkable |
| Discharge | Yellow-green, malodorous | “Cottage-cheese” like | Gray/White, “fishy |
| Wet mount | “Motile, flagellated protozoa | Nothing | Clue cells |
| KOH prep | Nothing | Pseudohyphae, spores | + whiff test |
| pH | Elevated (> 4.5) | Normal (4.0 – 4.5) | Elevated (> 4.5) |
| Treatment (non-pregnant) | Metronidazole | Topical or PO antifungal | Metronidazole |
| Treatment (pregnant) | Metronidazole | Topical antifungal | Metronidazole |
| Complications | Preterm birth, Low Birth Weight, PROM | None | Preterm birth, Low Birth Weight, PROM |
**normal vaginal discharge (**white, mucoid)
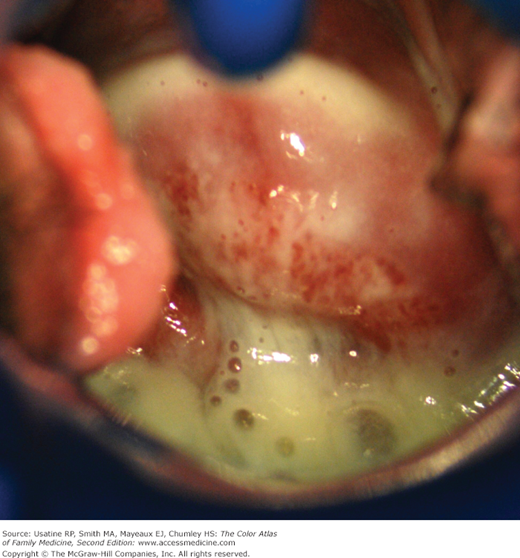
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is the most prevalent non-viral STD. Trichomonas has a predilection for epithelial cells. Most cases are asymptomatic. Men carry Trichomonads (upto 70% who have female partners with trichomoniasis) but are not affected. Trichomoniasis is a clinical marker for high-risk sexual activity and has a high co-incidence of infection with other STDs. Vertical transmission is posisble but rare
- Signs and symptoms
- Foul, thin yellow-green discharge
- Dysuria
- Dyspareunia
- Vulvar itching and burning
- Cervicitis may be present (can mimic chlamydial or gonococcal infection)
- Physical examination
- Erythematous, edematous vulva
- Excoriation
- “Strawbery spots”
- Investigation
- Saline prep: Motile trichomonads
- Vaginal pH: Elevated (> 4.5)
- Rapid Antigen Detection Tests
- Treatment
- Metronidazole
- Test for other STDs
- Refer sexual contacts for Metronidazole
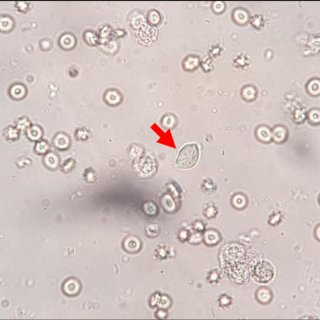
Candida Vaginitis
Candida vaginitis is not an STD but risk increases with sexual contact. C. albicans is the most implicated pathogens but other Candida species can cause it.

- Risk factors
- Diabetes mellitus
- Immunosuppression
- Recent antibiotic use
- Pregnancy
- Signs and symptoms
- Cottage-cheese-like or “curdy”discharge
- Vulvar/vaginal itching and burning
- Physical examination
- Erythematous, edematous vulva
- Excoriation
- Investigations
- 10% KOH prep: buds and hyphae
- Vaginal pH: normal (4.0 – 4.5)
- Criteria for complicated candida vaginitis
- Recurrent (≥ 4 cases per year)
- Severe
- Non-albicans infection
- Diabetic, Immunosuppressed, Debilitated or Pregnant
- Treatment of uncomplicated candida vaginitis
- Topical azole (Miconazole, Clotrimazole)
- Treatment of complicated candida vaginitis
- Recurrent: Prolonged PO Fluconazole
- Pregnant: Nystatin vaginal tablets
- Non-albicans: Boric acid vaginal capsules

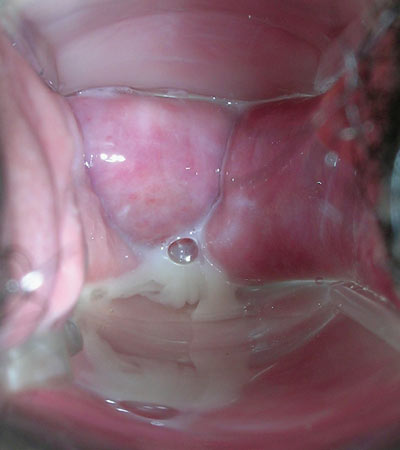
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is a disturbance in the normal vaginal flora. It is a disturbance, not inflammatory, and not an STD**.**
- Risk factors
- Vaginal douching
- Oral sex
- Sex during menses
- New or multiple sex partners
- Early sexual debut
- Sexual activity with other women
- IUD placement
- Smoking
- Signs and symptoms
- “Fishy” grey vaginal discharge without vaginal discomfort
- Physical exam
- Unremarkable
- Adherent gray discharge
- Investigations
- Saline prep: “Clue cells”
- Positive amine “whiff”” test (after adding KOH to the discharge sample)
- Elevated vaginal pH
- Treatment
- Metronidazole


