Viral hepatitis is a viral infection of the liver. It is most commonly caused by the hepatitis virus, but other viruses e.g. CMV, EBV and Yellow Fever can cause hepatitis. There are 5 types of hepatitis virus: Hepatitis A Virus (HAV), Hepatitis B Virus (HBV), Hepatitis C Virus (HCV), Hepatitis D Virus (HDV), and Hepatitis E Virus (HEV). HAV and HEV are spread fecal-oral. HBV, HCV, and HDV are spread parenterally (all body fluids are potentially infective) and can cause chronic infection. HEV can only cause chronic infection in immunosuppressed individuals. Only HAV and HBV have effective vaccination. All chronic hepatitis (B, C and D) increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
| HAV | HBV | HCV | HDV | HEV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Enterovirus | Hepadnavirus | Flavivirus | Incomplete virus | Calicivirus |
| Nucleic Acid | RNA | DNA | RNA | RNA | RNA |
| Incubation (weeks) | 2-4 | 4-20 | 2-26 | 6-9 | 3-8 |
| Spread | Fecal-oral | Parenteral | Parenteral | Parenteral | Fecal-oral |
| Acute or Chronic Hepatitis | Acute | Acute and Chronic | Acute and Chronic | Acute and Chronic (requires HBV) | Acute |
| Treatment | Support, self-limited | Support, Monotherapy if chronic, Follow-up for hepatocellular carcinoma | Combination therapy | Interferon alfa (limited success) | No specific treatment |
| Active immunization | Vaccine | Vaccine | No | Prevented by HBV Vaccine | No |
| Passive Immunization | Immune serum globulin | Hyperimmune serum globulin | No | – | No |
- Patient History
- Recent travel and other GI symptoms e.g. diarrhoea = Hepatitis A
- IV drug use and unprotected sexual contact = Hepatitis B and C
- Signs and symptoms Prodromal symptoms usually precede jaundice
- Fever
- Malaise
- Anorexia
- Nausea
- Right Upper Quadrant pain
- Jaundice
- Dark urine (bilirubin is lost in urine)
- Light-colored stool (less bilirubin enters the intestines)
- Differentials
- Alcohol or Drug-induced hepatitis: AST> ALT is usually alcohol or drug-induced hepatitis
- Investigations
- Liver Function Tests
- Elevated AST
- Elevated ALT
- ALT > AST
- Elevated Bilirubin
- Complete Blood Count
- Elevated WBC
- Hepatitis Serology (Hepatitis A, C, D, and E): best initial test to determine the etiology
- PCR-RNA for hepatitis C: represents activity level (viral load) for hepatitis C
- PCR-DNA for hepatitis D: represents viral load for hepatitis B
- Liver Function Tests
- Treatment of acute hepatitis
- Supportive
- Avoid alcohol and elective surgery
- Immunize contacts
- Treatment of chronic hepatitis B
- Monotherapy with Tenofovir, Lamivudine, Adefovir or Entecavir
- Started > 6 months of postitive surface antigen
- Long term monitoring of LFTs based on ALT, AST
- Monitor for hepatocellular carcinoma via ultrasound
- Interferon is falling out of favour
- Monotherapy with Tenofovir, Lamivudine, Adefovir or Entecavir
- Treatment of chronic Hepatitic C
- Genotype → Combination therapy Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir or glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
- Long-term monitoring of HCV RNA which indicates response
- Monitoring starts at diagnosis and is continued for 12 weeks
- Treatment is discontinued at 12 weeks is cured or continued indefinitely if chronic (80% of patients)
- Definitive cure of chronic hepatitis (cirrhosis)
- Transplantation
- Vaccination
- HAV vaccine is given to travelers, those living in crowded areas, and oral-anal sexual contact
- IM dose gives immunity for 1 year
- 20 years immunity if a booster is given at 6-12 months
- HBV vaccine is given to everyone
- HAV vaccine is given to travelers, those living in crowded areas, and oral-anal sexual contact
- Post-exposure prophylaxis
- HAV post-exposure prophylaxis
- Vaccinate if > 12 mos
- HAV immune globulin if immunocompromised or chronic liver disease
- HBV post-exposure prophylaxis
- HBV immune globulin is given after high risk exposure
- HAV post-exposure prophylaxis
Interpretation of Hepatitis A Serology
| Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Anti-HAV positive | Acute Hepatitis A |
Interpretation of Hepatitis C Serology
| Antibody | RNA | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Ab- | HCV RNA + | Infection |
| Ab+ | HCV RNA + | Infection |
| Ab + | HCV RNA – | Immunity |
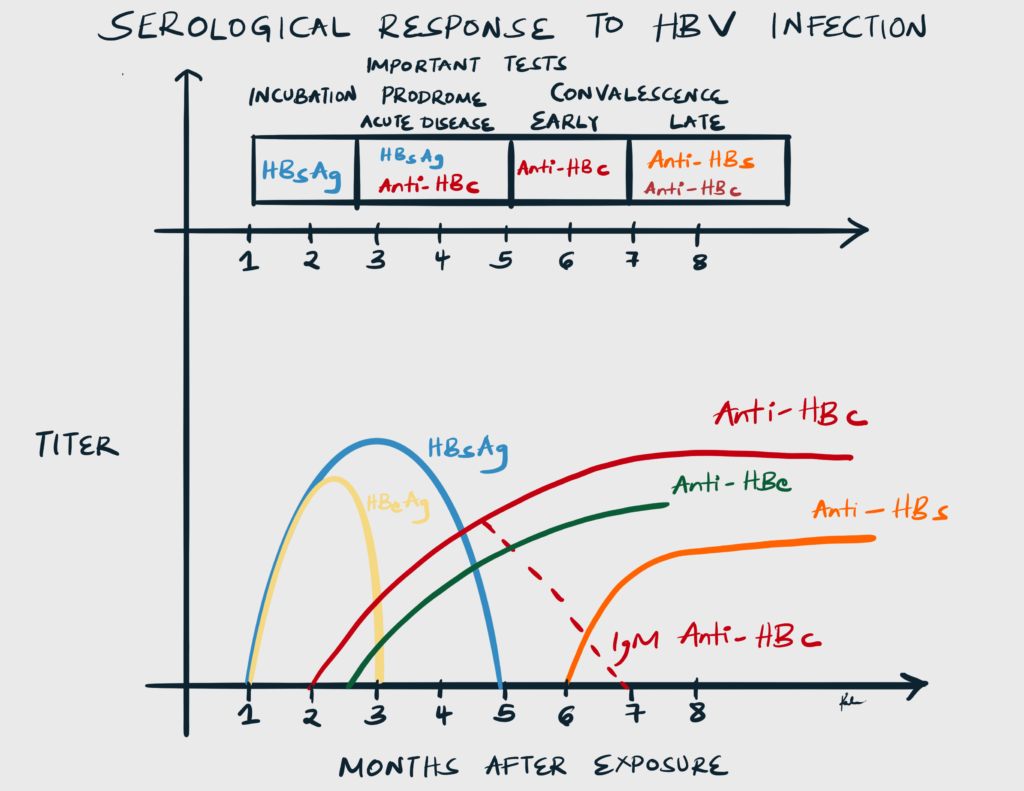
Interpretation of Hepatitis B Serology
| Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| HBsAg positive | Active Infection |
| HBeAb positive | Infectious |
| IgM HBc positive | Early infection |
| IgG HBc positive | Immune, Exposed |
| IgG HBs positive | Immune |