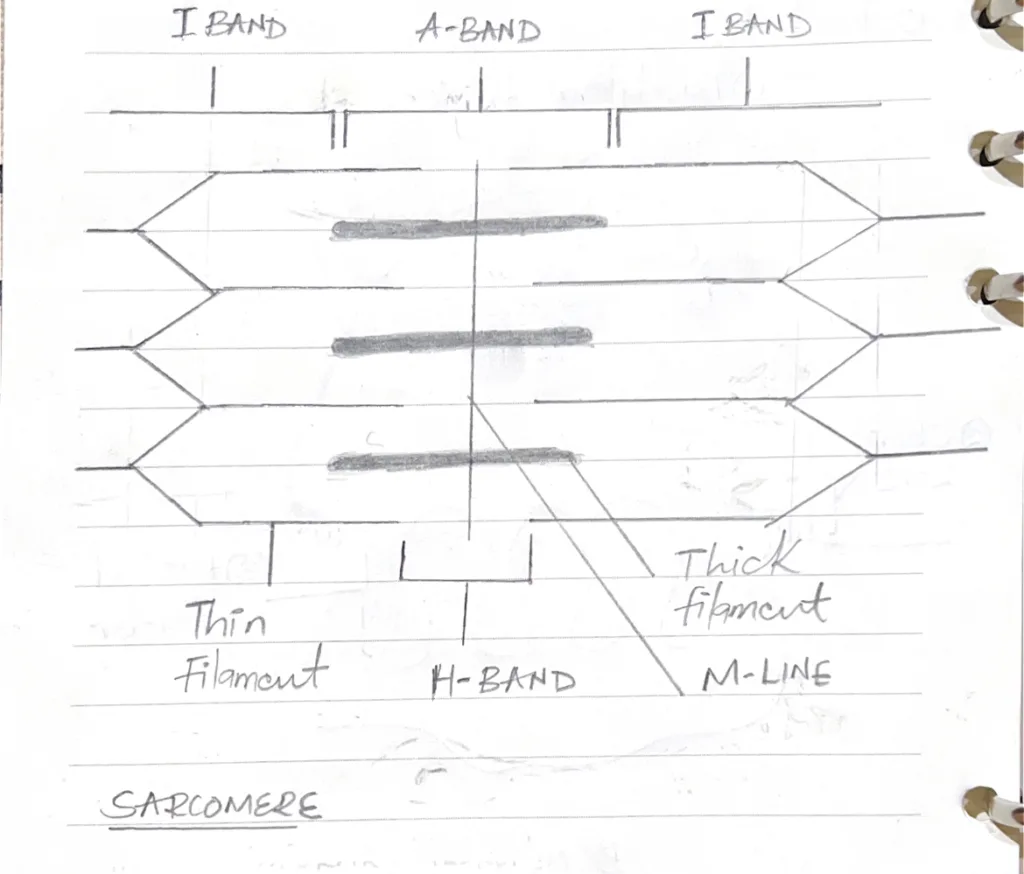
Illustrate the ultrastructural arrangement of contractile fibres in striated muscle
What are the structural components of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle
- Transverse components
- Fascia adherens (Adhering junctions): site of attachment of thin filaments (actin) between cardiac myocytes
- Macula adherents(Desomosomes): Re-enforce the fascia adherens and are found in both the transverse and lateral components of the intercalated disc
- Lateral components
- Gap junctions (Communicating junctions): Allows ions to diffuse between cardiac myocytes.

Distinguish between a diad and a triad in striated muscle
| Diad | Triad | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | T-tubule and 1 terminal cisterna of the sarcoplasmic reticulum | T-tubule and 2 adjacent terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum on either side |
| Location on the sarcomere | Z-line | Junction between A and I bands |
| Muscle | Cardiac muscles | Skeletal muscles |
| Function | Contraction of cardiomyocytes | Contraction of skeletal muscle and calcium ion secretion |
List the structural differences between skeletal muscles, cardiac muscles, and smooth muscles
| Skeletal muscle | Cardiac muscle | Smooth muscle | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Long tubular | Long branching | Spindle-shaped |
| Nucleus | Multinucleated | Uninucleated | Uninucleated |
| Striations | Present | Present | Absent |
| Location of nucleus | Periphery | Central | Central |
| T-tubules | Triads at A-I junction | Dyads at Z-disc | Absent |
| Sarcoplasmic reticulum | Abundant | Less abundant | Indistinct |
| Distinctive structural features | Highly organized sarcomeres and triads | Intercalated discs | Gap junctions, caveolae and dense bodies |